Achieve Low Rates on Export Finance Using the Interest Equalisation Scheme


What is the Interest Equalisation Scheme in India?
In international trade, access to affordable finance is a crucial factor that impacts the profitability of exporters. Recognising this, governments often institute schemes to support exporters in accessing finance at competitive rates.
Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) is one such scheme that provides pre and post-shipment credit to exporters at subsidised interest rates. It allows exporters easy access to credit and reduces their cost of borrowing.
Key Features of the Interest Equalisation Scheme
The Government of India launched The Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) on 1st April 2015. Initially, the scheme was valid for five years until March 31, 2020. However, it has undergone several extensions in response to evolving circumstances, including the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to a recent notification from the Reserve Bank of India, the government has extended the scheme until June 30, 2024. This extension offers specific benefits to various categories of exporters. Manufacturers and merchant exporters dealing with specified 410 HS lines will be entitled to a 2% interest equalisation rate. Additionally, MSME manufacturers exporting under any HS line will receive a higher rate of 3%.
Eligibility Criteria for the Scheme
Eligible Exporters and Industries by HS code
Exporters can identify eligibility based on industry classification using Harmonised System (HS) codes. These codes categorise export products into specific industries, determining their eligibility for the scheme. The scheme extends to specific export products meeting predefined criteria, ensuring that it targets industries with significant export potential.
Official channels, such as the Indian trade portal, provide a comprehensive list of eligible exporters and industries and the corresponding interest equalisation rates. Below are some covered sectors:
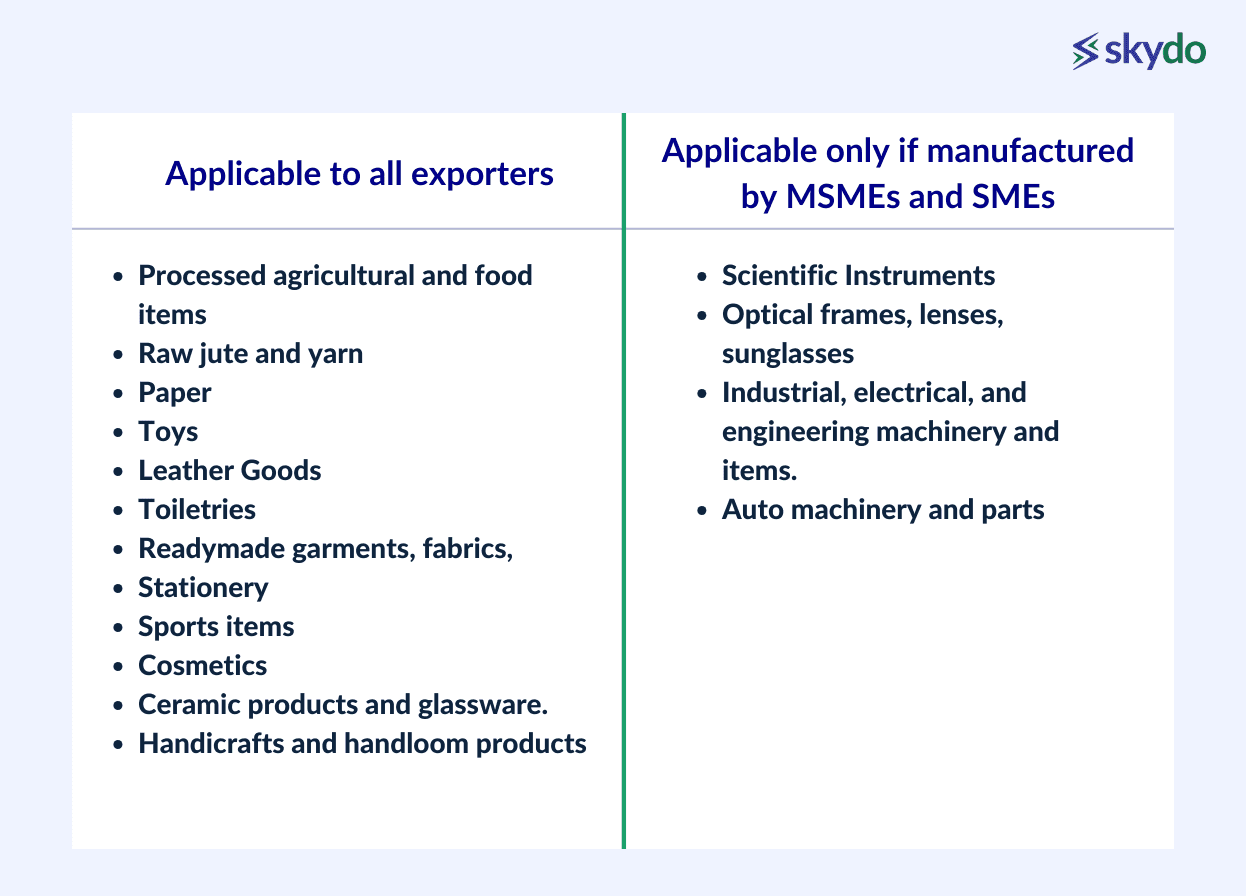
Criteria for Export Products under the Scheme
Exports under the scheme must originate from India. The Rules of Origin in the Foreign Trade Policy 2015-20 outlines the minimum processing criteria to qualify as ‘originating from India.’ These include:
- The exporter must manufacture the goods following the definition of 'manufacture' provided in the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP).
- When an exporter uses inputs that have been imported, the final exported products can be considered as originating in India. However, these products must undergo substantial processing or operations within India, as specified in the Handbook of Procedures.
- Telecom exports are contingent upon meeting the minimum value addition percentage (providing services beyond the core skills such as calling and SMS) specified by the Department of Telecommunications.
Step-by-Step Guide to Avail the Scheme

1. Auditor's Certification:
- Engage an external auditor to certify your eligibility for the scheme. The certification ensures that the benefit is for genuine beneficiaries.
- Submit this certification to their respective bank and any other required documentation as part of the application process.
2. Benefits Disbursement:
- Banks evaluate exporters' eligibility and verify compliance with industry classification, export turnover, and adherence to the rules of origin.
- Upon verification, the bank disburses the interest equalisation benefits to the eligible exporter. The disbursed benefit is typically provided upfront to the exporter, reducing the interest burden on their export loans.
- Banks monitor compliance with the scheme's guidelines and regulations throughout the process. They maintain records of disbursements and ensure that all transactions follow the prescribed procedures.
3. Reimbursement Claim:
- After disbursing the benefit to the exporter, the bank initiates a reimbursement claim with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The claim includes details of the disbursed amount and supporting documentation.
- The external auditor's certification serves as crucial validation for the bank's reimbursement claim to the RBI. It confirms the exporter's eligibility and enhances transparency and accountability in the reimbursement process.
Registration Process for New Applicants
New applicants can successfully register for the scheme by following these steps:
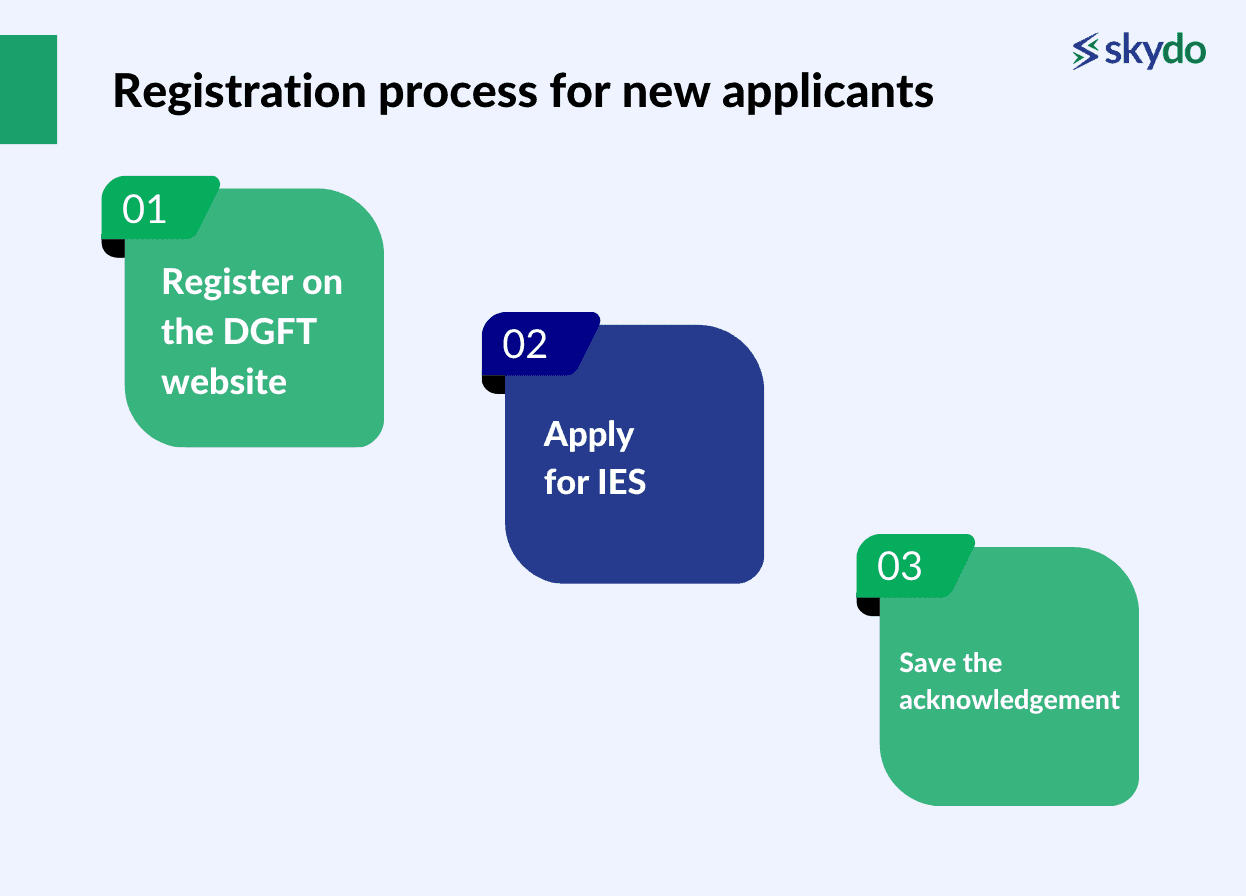
- Register on the DGFT Website: Register on the Directorate General of Foreign Trade website and link your Importer Exporter Code (IEC) with your account.
- Apply for IES: Once registered, log in to your account on the DGFT website and navigate to the IES section. Fill in the necessary details in the application form.
- Save the Acknowledgement: After applying, save the acknowledgment bearing the UIN. Proceed to pay the user charge fee for generating the UIN. You can make the payment through any available online payment modes. The UIN is valid for one year from the registration date. During this one-year validity period, exporters can submit applications for the scheme.

Documentation Required for Application

- Business Registration Documents: Businesses must provide proof of their business registration, including certificates of incorporation, business licenses, and other relevant documents.
- Export Turnover Details: Exporters must furnish details of their export turnover, including historical data and projections.
- Industry Classification Information: Exporters must specify their industry classification based on the Harmonized System (HS) codes, which categorise export products into specific industries.
- Additional Documentation: Depending on the scheme's specific requirements and the exporter's circumstances, exporters may need to submit additional documentation, such as financial statements, export performance reports, and tax records.
Financial Implications and Benefits
One significant advantage of the Interest Equalization Scheme is its ability to lower borrowing costs for eligible exporters.
For example, XYZ Exporters, a medium-sized enterprise specialising in the export of textiles, is seeking export credit. If it takes credit from banks, it will have to pay the base interest + 3%-5% above the base rate. However, if it’s eligible for the Interest Equilisation Scheme, it can get export credit at a subsidized 3% interest rate.
The concessional interest rate enables them to lower their overall financing expenses and improve their profitability.
Furthermore, XYZ Exporters could offer more competitive pricing in the international market, attracting more customers and expanding their market share. They could redirect saved funds toward business expansion initiatives, product diversification, or enhancing operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Interest Equalisation Scheme in India provides exporters access to affordable finance. By subsidising interest rates on bank loans, the scheme effectively reduces borrowing costs, empowering exporters to optimise their financial resources and expand their business operations.
For eligible exporters, the time is now to explore the IES's benefits and take proactive steps toward gaining them. By initiating the registration process, engaging with relevant authorities, and adhering to the scheme's guidelines, exporters can unlock opportunities to lower financial burdens, improve competitiveness, and drive sustainable growth.

Q1. How Frequently Can One Apply for the Scheme?
Ans: Applicants can apply for the scheme based on their business needs and eligibility criteria.
Q2. Is the Scheme Applicable to All Export Goods?
Q3. Till When Is the Scheme Valid?
Q4. What to Do in Case of Rejection of Application?
Q5. What Is the Limit per Exporter?
Q6. What’s the Limit of the Overall Scheme?
Q7. Which Banks Are Actively Involved in Deploying the Scheme?
Q8. Who Is Not Eligible for Any Benefit?