Export Invoices: Should I Invoice in INR or Foreign Currency?


You've just bagged a project with an international client, and now it’s time to get hustling. However, you need to raise an export invoice for 50% of the advance amount. How should you present your charges? Should you opt for the comfort of your native Indian Rupee (INR) or invoice in foreign currency?
The quick answer to this is you should invoice in the currency of your client - say if your client is based in the US, you should invoice in USD, however there are other considerations which can significantly affect costs, fees, tax compliance, and financial management.
Let’s delve into the complexities of international transactions and explore factors to consider when deciding whether to invoice in Indian Rupees (INR) or a foreign currency. Additionally, we will shed light on the relevance of SWIFT, LUT, FIRA, and FIRC in navigating the payment process for international transactions.
Before deciding on the invoicing currency, you must consider the costs and fees associated with international transactions.

1. The Volume of Work and Related Costs
As the volume increases, your business may benefit from economies of scale, enabling you to negotiate better rates with service providers and suppliers. Higher transaction volumes can also justify investments in streamlined processes and technologies that enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
2. Client’s Location
If you are servicing clients from the US or UK, it is more straightforward and convenient to bill in that currency as it provides better financial stability and credibility. However, you can bill in your local currency if it is stable.
3. Transaction Costs
International payments generally include intermediary bank fees, transaction fees, conversion fees, and other administrative charges levied by financial institutions or payment service providers for additional transactions or payment-related services
Let's say you are a tech export business based in India sending an invoice to clients in the United States. Suppose your invoice is in USD, and your bank charges high fees for currency conversion. In that case, it may be more cost-effective to invoice in INR with an export payments partner like Skydo to minimise transaction costs and ensure that you receive the maximum possible amount. Skydo charges a flat fee for each transaction.
4. Tax Implications of Charging in Different Currencies
Sending an invoice in INR may subject the trade to Goods and Services Tax (GST) based on the nature of the transaction and relevant thresholds. As an IT services exporter, accepting foreign payments in INR will be subject to 18% GST. Therefore, you will need to add that tax amount to your invoice.
Conversely, invoicing in a foreign currency might have different tax implications, such as potential exemptions or other GST treatment. For example, if you accept the payment in USD, you must submit a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) (explained further in the article) per government regulations. Read more about the taxation rules and regulations concerning foreign transactions here.
5. Currency Exchange Rate Risk
International transactions expose businesses to currency exchange rate fluctuations, which can impact the value of transactions and profitability. Swings in exchange rates can result in potential gains or losses, affecting the overall cost of the transaction and financial performance.
6. Competitive Positioning in Foreign Market
Business in foreign markets often entails additional costs to establish and maintain a competitive position. These costs can include market research, advertising and marketing expenses, customisation of products or services to suit local preferences and investments in distribution channels. Such expenditure is necessary to penetrate and compete in foreign markets effectively.
7. Accounting and Reporting Considerations
International transactions necessitate compliance with accounting and reporting standards specific to each jurisdiction. It involves additional administrative efforts, such as preparing financial statements according to local regulations, adhering to tax reporting requirements, and potentially engaging with local accounting professionals to ensure compliance.
8. Legal and Regulatory Compliances
Engaging in international transactions requires businesses to navigate various legal and regulatory frameworks in different jurisdictions. It may include understanding and adhering to foreign trade regulations, customs requirements, import/export laws, intellectual property protection, and other legal obligations. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to penalties, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
9. Customer Preferences
Assess the preferences of your international clients. Some clients may prefer invoices in their local currency to simplify accounting and budgeting processes. Others may be open to invoicing in your local currency. Understanding your clients' preferences will help you determine the most suitable invoicing approach that’s also profitable for your business.
Once the decision regarding the invoicing currency is final, the next step is determining the appropriate payment methods for international transactions.
Payment Methods for International Transactions
Several payment options are available, each with its advantages and considerations.
Businesses should evaluate payment methods based on transaction fees, processing time, safety, and customer preferences to make informed decisions.
Bank transfers, credit cards, online payment platforms, and letters of credit are among the popular choices.
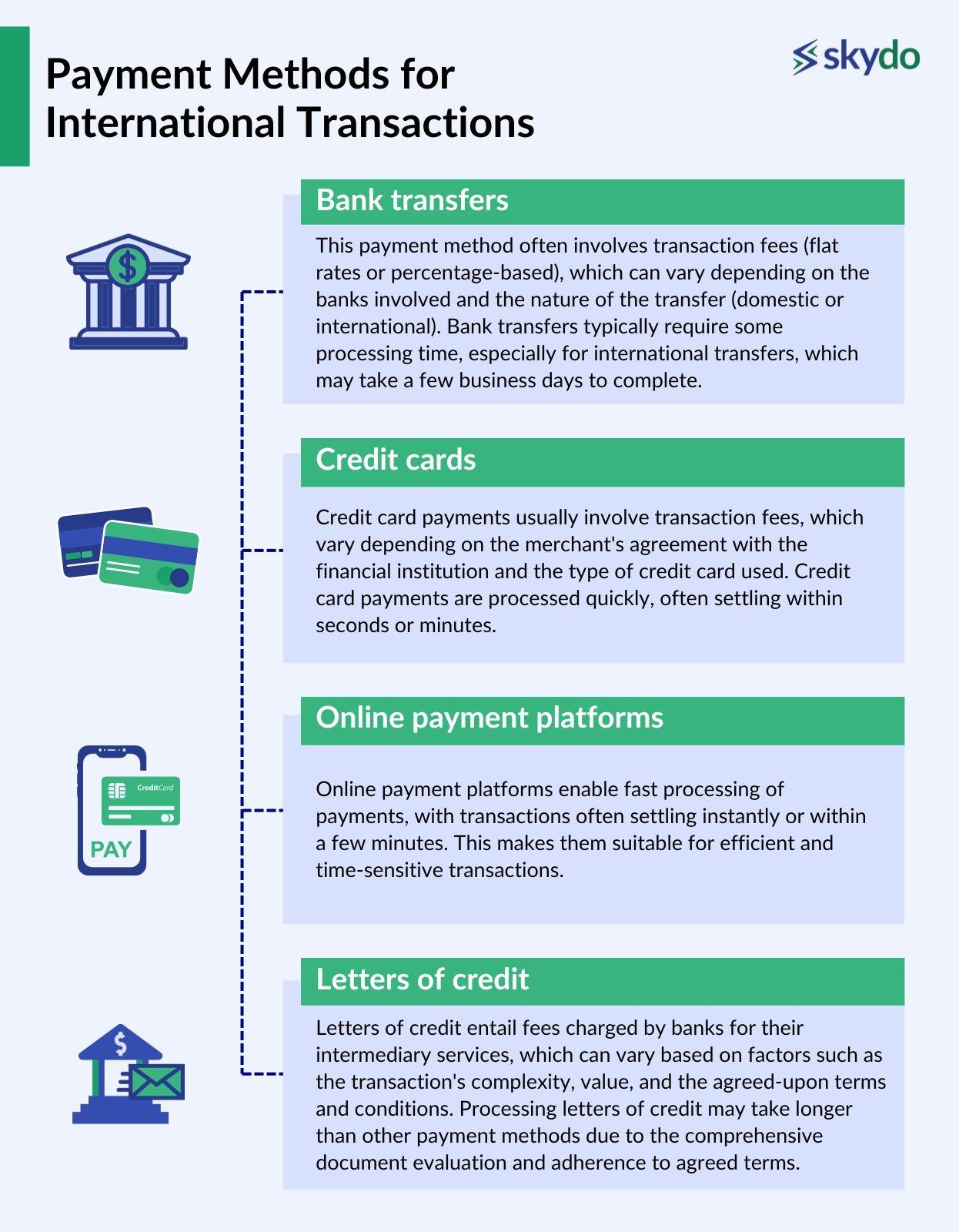
1. Bank transfers
This payment method often involves transaction fees (flat rates or percentage-based), which can vary depending on the banks involved and the nature of the transfer (domestic or international). Bank transfers typically require some processing time, especially for international transfers, which may take a few business days to complete.
They offer a level of safety as they typically require authentication and verification processes to initiate the transfer, reducing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
Businesses and individuals favour bank transfers if they have established relationships with their banks, for larger transactions, or when payment needs to be directly transferred to a specific bank account.
2. Credit cards
They are popular among consumers for their simplicity, ease of use, and convenience. Credit card payments usually involve transaction fees, which vary depending on the merchant's agreement with the financial institution and the type of credit card used.
Credit card payments are processed quickly, often settling within seconds or minutes. This makes them suitable for time-sensitive transactions or situations where immediate payment confirmation is required.
They also provide a certain level of safety as they are protected by fraud prevention measures and dispute resolution mechanisms provided by credit card companies.
3. Online payment platforms
These platforms charge transaction fees that can vary based on the platform and the type of transaction, either as a fixed amount or a percentage of the transaction value.
Online payment platforms enable fast processing of payments, with transactions often settling instantly or within a few minutes. This makes them suitable for efficient and time-sensitive transactions.
These providers also prioritise security and employ encryption technologies to protect sensitive financial information.
Online payment platforms have gained popularity due to their global accessibility, secure transactions, and ease of use. They cater to diverse customer preferences, particularly e-commerce transactions, international payments, and peer-to-peer transfers.
4. Letters of credit
Letters of credit entail fees charged by banks for their intermediary services, which can vary based on factors such as the transaction's complexity, value, and the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
Processing letters of credit may take longer than other payment methods due to the comprehensive document evaluation and adherence to agreed terms. The processing time can vary from days to weeks, depending on communication efficiency and document exchange.
By involving banks as intermediaries, they mitigate the risk of non-payment or non-delivery of services by ensuring that funds are held in escrow until specified conditions are met.
Letters of credit are frequently utilised in international trade, especially for sizable transactions or when enhanced financial security is desired. They are preferred by businesses operating in regions with limited payment infrastructure or when trust and assurance play vital roles.
As of 2021, SWIFT has enabled immediate processing between over 4 billion accounts and 11,000 institutions across more than 200 countries while upholding unmatched security, dependability, and robustness. Thus, businesses prefer to use SWIFT for money transfers and here’s all you need to know about it.
Understanding SWIFT in International Money Transfers
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) is a messaging network that enables global secure and standardised communication between financial institutions.
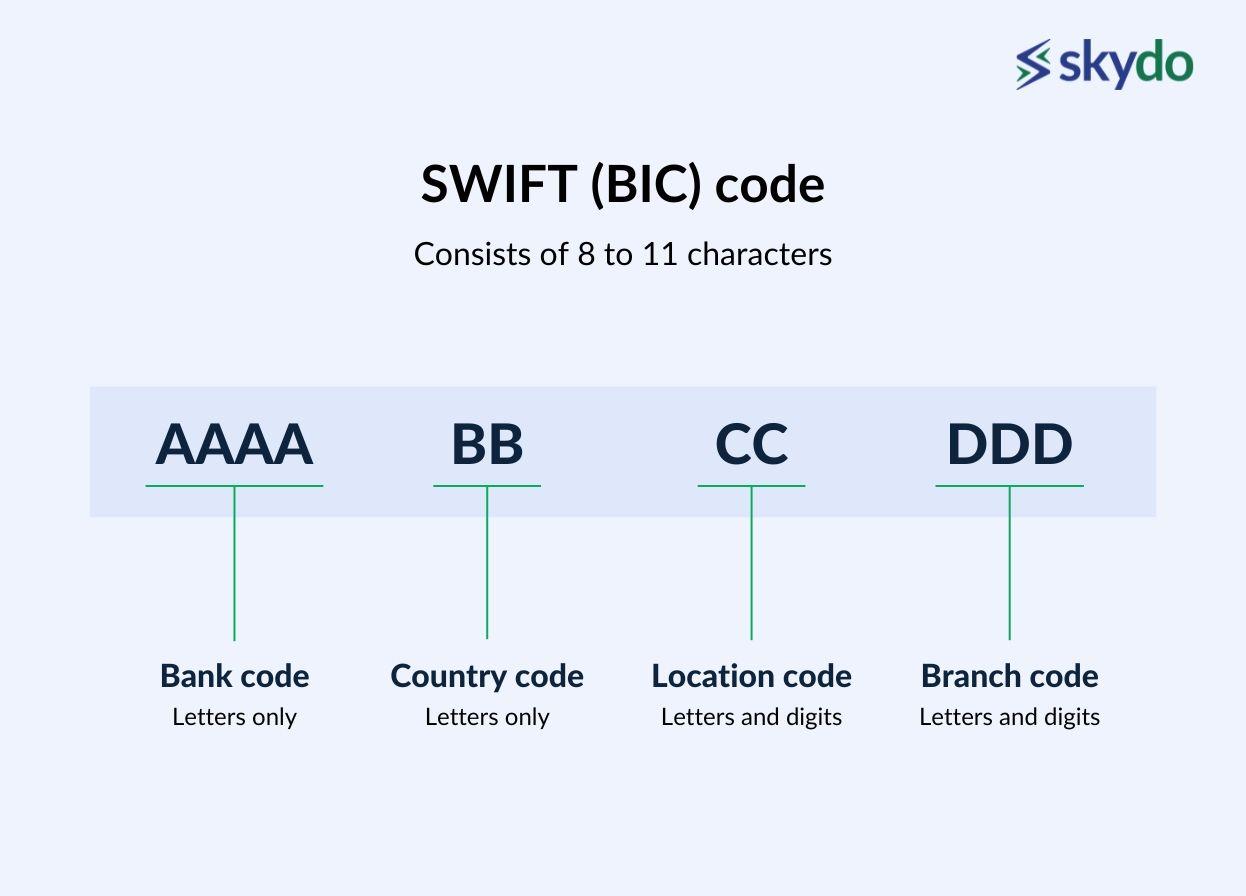
SWIFT assigns a unique identification code (or the SWIFT/BIC code) to each financial institution, allowing for accurate funds routing. It also utilises the SWIFT message format, which includes various fields containing transaction details. The syntax/interpretation is as follows.
First four characters: the institute code
The Next two characters: the country code
The Following two characters: the location/city code
The Last three characters: these are optional, but organisations use them to assign codes to individual branches.
One required field in the SWIFT message is field 71A, which highlights handling intermediary bank fees.
International money transfers through SWIFT typically take several business days due to factors such as time zone differences, intermediary bank involvement, and potential manual processing steps. The processing time can vary depending on the participating banks and the specific requirements of the transfer.
Additionally, SWIFT transactions involve fees charged by the participating banks. The sender is usually responsible for covering these fees, which can vary depending on the institutions involved, the transfer amount, and the transferring currency.
Payers have three options when making a SWIFT international transfer: SHA, BEN, and OUR. These options determine the distribution of charges between the sender and the recipient.
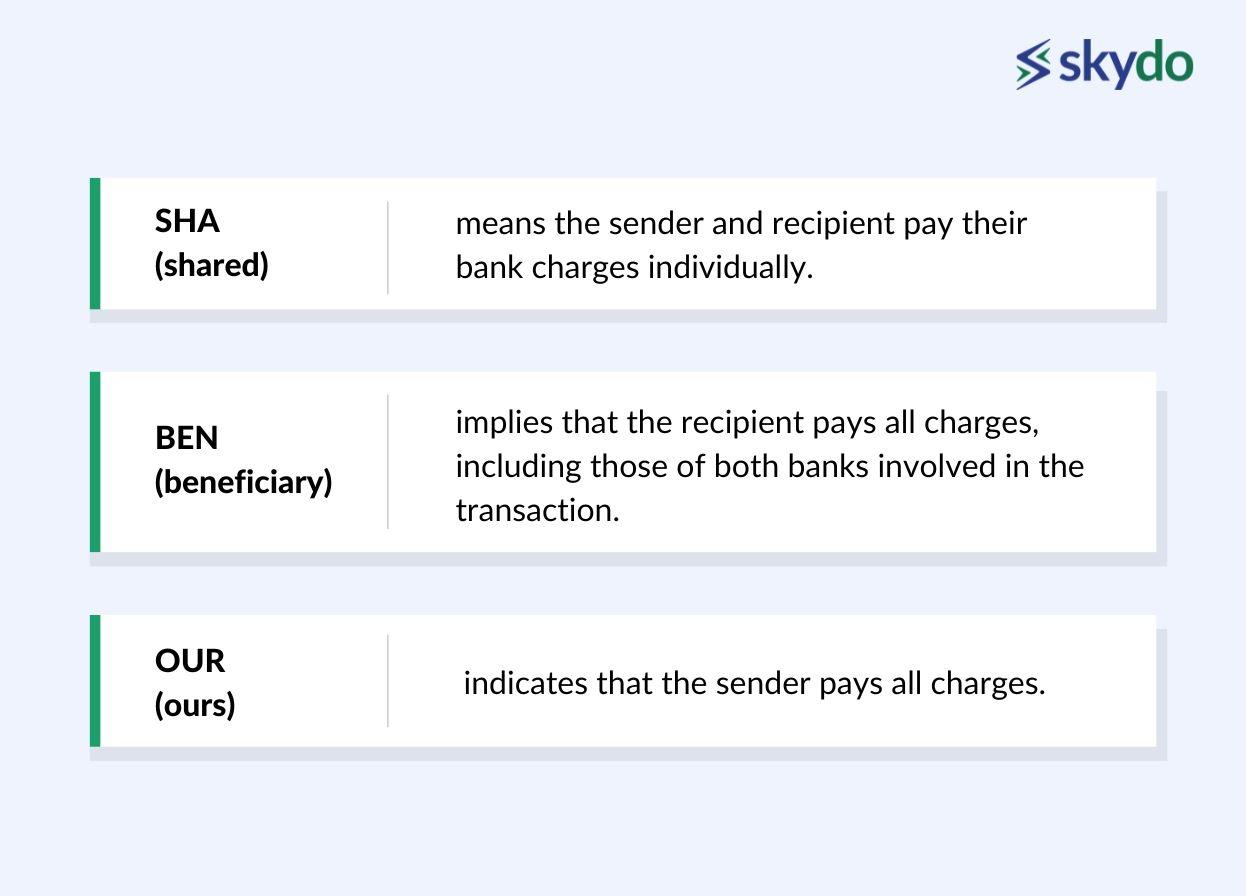
- SHA (shared) means the sender and recipient pay their bank charges individually.
- BEN (beneficiary) implies that the recipient pays all charges, including those of both banks involved in the transaction.
- OUR (ours) indicates that the sender pays all charges.
Deciphering these options is crucial to understanding the cost-sharing arrangement and making an informed decision based on the transaction value, relationship with the counterparty, and cost considerations.
However, once these transactions are successful, you need to ensure tax compliance with the FIRA/FIRC document.
Foreign Inward Remittance: FIRA and FIRC
FIRA (Foreign Inward Remittance Advice) and FIRC (Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate) are vital documents in international business transactions. They are often used interchangeably to refer to documents that serve as proof of inward remittance.
This document provides details such as the beneficiary, remittance amount, and purpose of payment. These documents are essential for maintaining transaction records, ensuring compliance with applicable laws, and facilitating the monitoring and regulation of foreign exchange transactions.
While FIRA and FIRC may have slight differences in terminology and format depending on a country's specific banking practices or regulatory requirements, their primary purpose remains – to provide evidence of foreign inward remittances receipt.
Per the RBI rulebook on the Export of Goods and Services, “AD bank should be satisfied with the bona fides of the transaction and export documents, such as export invoice / FIRC”. Additionally, “Further, AD Category – I banks need to report the electronic FIRC to EDPMS wherever such FIRCs are issued against inward remittances.”
Skydo simplifies obtaining GST-compliant FIRA and LUT by allowing you to download this vital document from its online platform, eliminating manual paperwork, streamlining the submission process, and ensuring compliance with GST regulations. This convenience and efficiency save time and resources, allowing you to focus on core activities and improve operational efficiency.
Here’s why you need a LUT.
The Importance of Letter of Undertaking (LUT) in International Transactions
The Letter of Undertaking (LUT) holds significant importance for GST-compliant-registered businesses supplying services outside India. LUT is a document that exempts your company from paying GST on export services and allows for a smooth flow of transactions. It serves as a legal undertaking by the exporter to fulfil specific obligations and comply with GST regulations.
Obtaining a valid LUT is essential for businesses engaged in international transactions as it enables them to provide services without charging GST, making their offerings more competitive in the global market. Failure to provide a valid LUT may lead to unnecessary GST liability and compliance issues, impacting the financials and overall business operations.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of international transactions requires careful consideration of various factors, such as costs, fees, tax implications, payment methods, and regulatory compliance. Deciding whether to invoice in INR or a foreign currency can significantly impact a business's financial management and profitability.
Understanding the role of SWIFT, LUT, FIRA, and FIRC in international transactions is essential for businesses engaged in cross-border trade. By comprehending these concepts and their interplay, you can streamline payment processes, minimise costs, ensure tax compliance, and establish healthier financial controls.
FAQs
Q1. What is a valid currency for an invoice in India?
Ans: In India, an e-invoice for export must be issued in Indian Rupees (INR) as the official currency. Foreign currencies are not accepted for domestic transactions, ensuring compliance with the country's legal and financial regulations.
Q2. Could I prepare an invoice using any currency in an export business?
Ans: Yes, in the export business, invoices can be prepared using any internationally recognised currency. This flexibility allows exporters to adapt to the preferences and regulations of their international clients.
Q3. Do exporters want to invoice in the importers' currency?
Ans: Exporters often prefer invoicing in the importers' currency to simplify transactions and accommodate the preferences of their international clients. It helps in avoiding currency exchange rate uncertainties and making transactions more transparent.
Q4. What is an export invoice?
Ans: An export invoice is a document issued by a seller to an international buyer detailing the products or services sold, their quantities, prices, and other relevant information. It serves as a formal request for payment and is a crucial document in international trade and compliance.