GST Requirements for International Service Sales


It’s 2017. You’re creating an invoice for your software services to a client, and you add VAT/Sales tax before you complete the total. It seems straightforward, but is it really?
Let’s understand how tax used to work before and after GST, how GST works for export businesses, GST Compliance and Export Services, input tax credit, and how to claim GST refunds.
Previous tax structure vs new tax structure
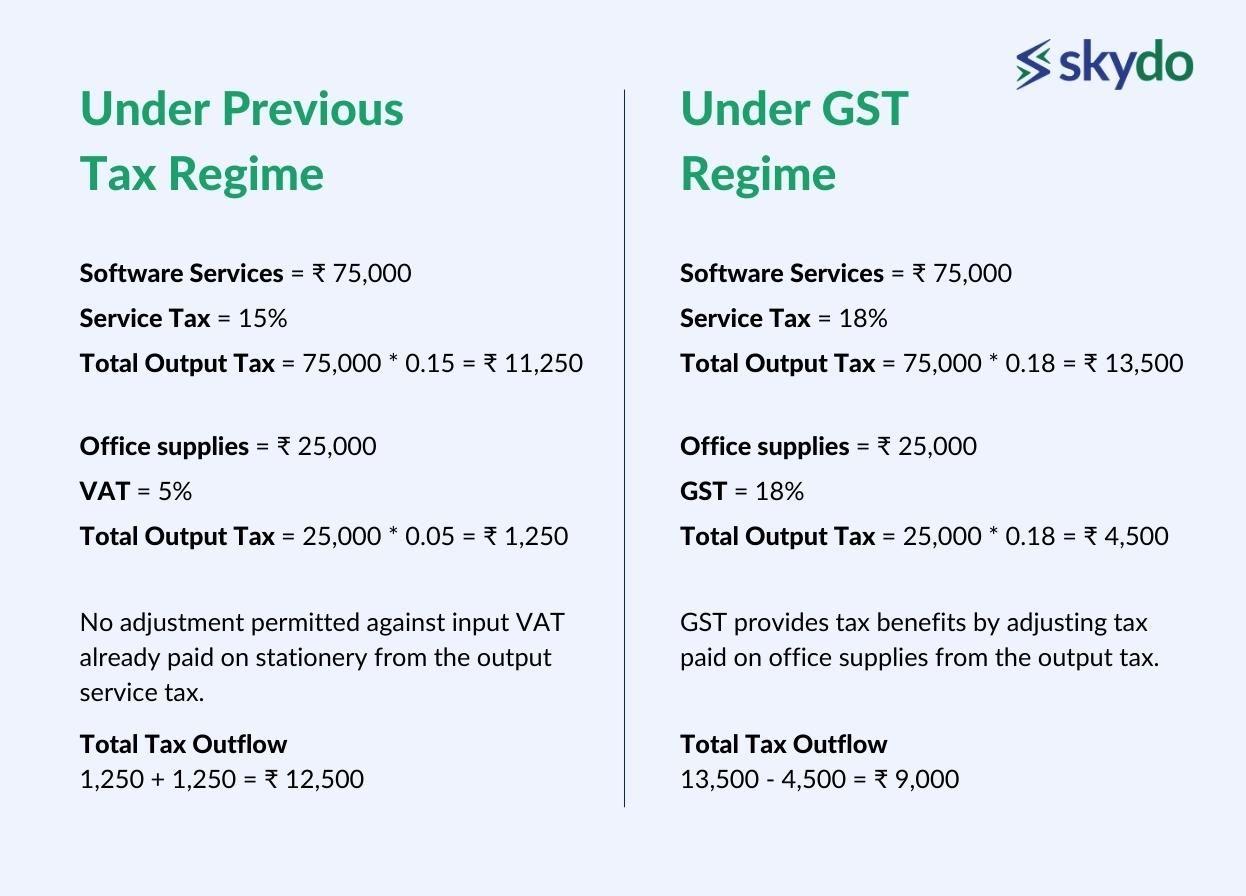
Under the previous regime, you would have charged a 15% service tax on services worth Rs. 75,000. Then, your output tax would be Rs. 11,250. But, if you purchased office supplies for Rs. 25,000 and paid 5% as VAT, the input tax would have been Rs. 1,250.
However, you couldn't adjust the input VAT already paid on stationery from the output service tax. Consequently, the total tax outflow would have been Rs. 12,500.
But, after the GST implementation, you would charge 18% GST on services worth Rs. 75,000, which amounts to Rs. 13,500. Subtracting the GST on office supplies (Rs. 25,000 x 18%) equals Rs. 4,500. Your net GST liability would be Rs. 9,000.
The introduction and implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) eliminated the previous cascading effect of “tax on tax” created by several other indirect taxes in India, including excise duty, VAT, and services tax.
It made the lives of CAs easier, and it was easier for an aspiring entrepreneur to follow their dream and start a business without the nightmare of multiple tax filings.
Four GST types exist–
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
- Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
Each type imposes different tax rates on the buyer's end.
Filing these GST returns requires a business to register through the GST portal. Once the registration is complete, you get a GSTIN, a unique 15-digit identification number assigned to registered taxpayers under the GST regime in India. It plays a crucial role in tracking transactions and ensuring tax compliance. It further enables the government to monitor the movement of goods nationwide and verify business tax payments.
Understanding GSTIN Registration for Export Businesses
A business’s GSTIN registration is subject to certain thresholds and exemptions, particularly if its turnover exceeds in the following cases.
- Rs. 40 lacs or higher for the manufacturing sector
- Rs. 20 lacs or higher for the services sector
- Rs. 10 lacs or more for particular category states
A GSTIN also allows businesses to claim input tax credits on their purchases, reducing their overall tax liability.
This identification number needed for GST and for your business also requires filing periodic returns, which may vary based on the nature of your business and its turnover. These returns include details of sales, purchases, input tax credits, and output tax liabilities. The frequency of filing returns can range from monthly to quarterly or annually, depending on the turnover threshold.
You can file these tax returns through the GST portal, the official government platform for GST-related activities. You must file these returns within the specified due dates to avoid penalties or late fees.
Recently, the government of India also announced a new threshold for e-invoicing, requiring businesses with an annual turnover of over Rs. 5 crores to adopt the e-invoicing system. This system requires companies to generate invoices in a standard electronic format and upload them to a central portal.
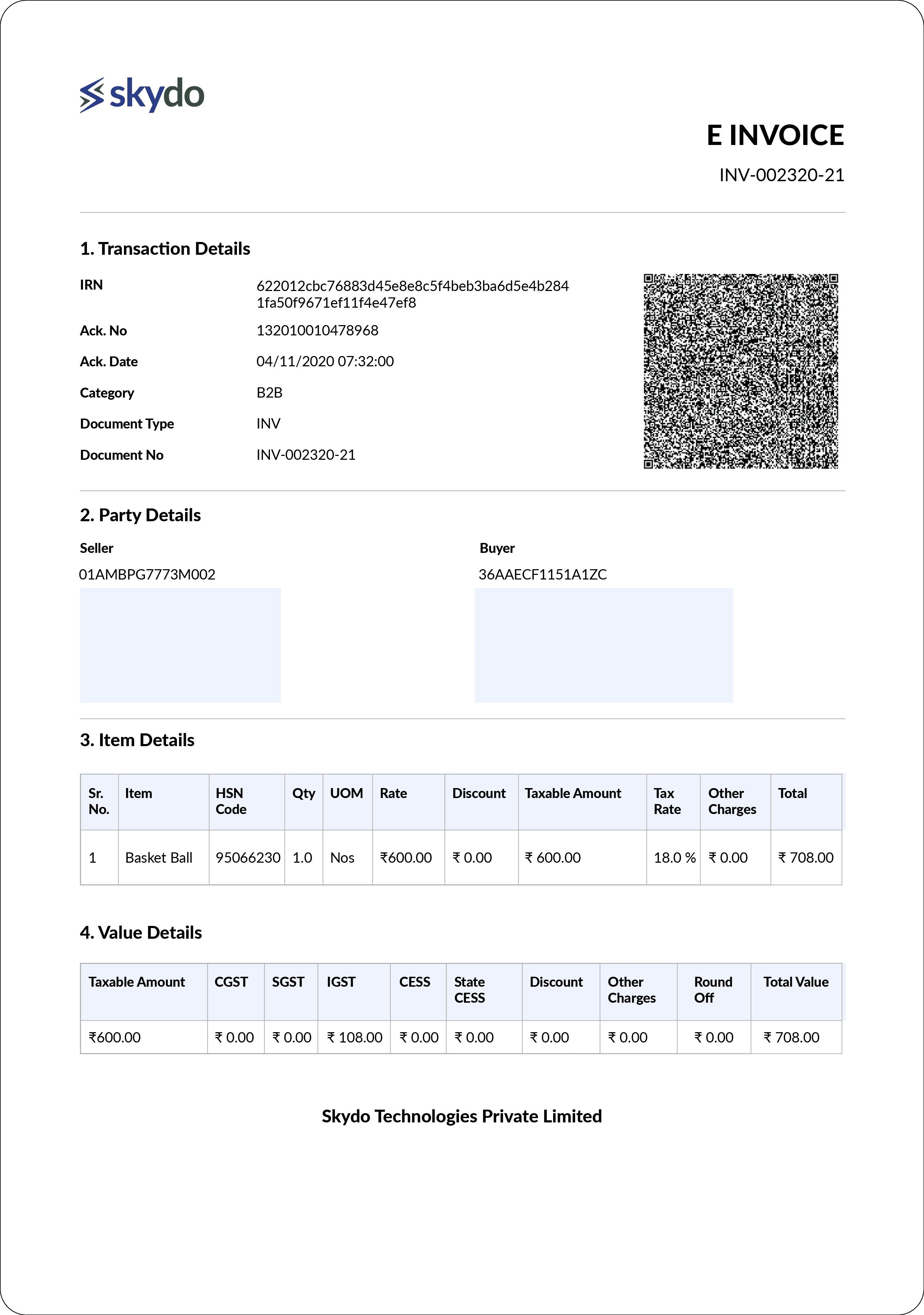 E-invoice Template Sample
E-invoice Template SampleConsidering the volume of transactions involved in a business with such a considerable turnover, the e-invoicing system aims to reduce errors, increase accuracy and efficiency, provide real-time validation, improve cash flow management, and enhance tax administration.
However, as a business providing your services abroad, how do you navigate this tax, and does it apply to the services you provide worldwide? Let’s find out.
Treatment of GST for exports
Under the GST regime, export services are considered "zero-rated supplies'', meaning a supplier can supply without payment of GST if they have submitted the LUT or with payment of GST and then get a refund once the goods are exported.
However, to claim refunds on the taxes paid on their inputs, they must register for GSTIN. Additionally, GSTIN registration provides several benefits for export service businesses, including having access to input tax credits.
GST Compliance for Export Services
The compliance and documentation for an export services business defer based on whether you accept payments in foreign or Indian currency. The steps in both scenarios are as follows.
1. Foreign Currency Transactions
If the business accepts payment in foreign currency for services rendered abroad, no GST applies. However, the government requires you to justify this amount which requires submitting a Letter of Undertaking (LUT).
A LUT must be furnished with Form GST RFD-11 per rule 96A, wherein they declare their commitment to meet all the prescribed GST requirements for exporting goods without making an IGST payment.
According to the CGST Rules, 2017, registered individuals can submit an Export bond or LUT (Letter of Undertaking) in Form GST RFD-11 to export goods or services without paying the integrated tax.
They are eligible to apply for an LUT if they are registered under GST and intend to supply goods or services within India, overseas, or to Special Economic Zones (SEZs) without the requirement of paying the integrated tax.
If you fail to provide the LUT, you must pay IGST or furnish an export bond.
2. Indian Currency Transactions
Foreign exchange transactions are subject to 18% Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. These transactions include activities such as remittance, currency exchange, or any other conversion of one currency to another.
To comply with GST regulations, businesses engaged in foreign exchange transactions are required to file certain forms. These forms are as follows.
- GSTR-1: This form reports outward supplies of taxable goods and services. It includes details of foreign exchange transactions made by the business.
- GSTR-3B: This form is a summary return where businesses declare their GST liability and claim Input Tax Credit. It includes information about the GST payable on foreign exchange transactions.
- GSTR-9: This annual return form summarises all GST transactions made during the financial year. It includes information related to foreign exchange transactions.
- GSTR-9C: This form applies to businesses with an annual turnover above a specified limit. It reconciles the information provided in GSTR-9 with the audited financial statements.
GST payments and refunds
GST rates
The rates under GST are categorised into different tax slabs based on the type of goods or services being supplied, as shown in the table below.

Additionally, specific goods and services, such as petroleum products, alcoholic beverages, and electricity, are kept outside the purview of GST and are subjected to separate taxes by the respective state governments. Some luxury items and sin goods may attract an additional cess on top of the applicable GST rate.
Input Tax Credit (ITC)
The Input Tax Credit (ITC) allows businesses to claim credit for taxes on inputs used in producing goods or services and offset the GST liability on the output. It reduces their overall tax liability and costs, encourages tax compliance and enhances the competitiveness of businesses.
However, they must ensure compliance with the GST rules and maintain proper documentation to support their ITC claims.
1. Eligibility for ITC
Businesses must register under GST and use or intend to use the claimed input goods or services for business purposes, not personal use.
2. Conditions for Claiming ITC
To claim ITC, businesses must ensure that their suppliers have reported the supplies accurately and filed their GST returns. The recipient of goods or services must possess a valid tax invoice or debit note issued by the supplier.
The recipient must have received the goods or services. The supplier must have paid the GST charged to the government on the supply.
3. Types of Inputs Eligible for ITC
- Goods: Raw materials, semi-finished goods, finished goods, and other goods used in the production or supply of goods or services.
- Services: Professional fees, rent, logistics, advertising, maintenance, and other services used for business purposes.
- Capital Goods: Purchases of machinery, equipment, vehicles, furniture, and other capital goods used for business purposes.
- Input Services: Legal, accounting, consulting, transportation, and other services used in business operations.
4. Restrictions and Blocked Credits
You cannot claim ITC on goods and services used for personal purposes, exempt supplies, and non-business purposes. Additionally, you cannot claim ITC on specific goods or services for which a composition scheme has been opted.
How to pay GST and claim refunds
GST payments can be made online through the GST portal using a bank account or credit/debit card. Other ways include the following.
- Credit Ledger: Dealers can utilise Input Tax Credit (ITC) for GST payment, but only for taxes and not for interest, penalties, or late fees. ITC is available in the credit ledger, and you can use it when generating the GST payment challan.
- Cash Ledger: You can make GST payments online or offline. You must generate a challan on the GST Portal for both modes. Online payment is mandatory for tax liabilities exceeding Rs 10,000 and can be made through Internet banking, cards, or NEFT/RTGS. Offline payment can be made at authorised banks using cash, cheques, or demand drafts.

GST Refunds
Under GST, there are various circumstances in which businesses can claim a refund. Here are some common cases.
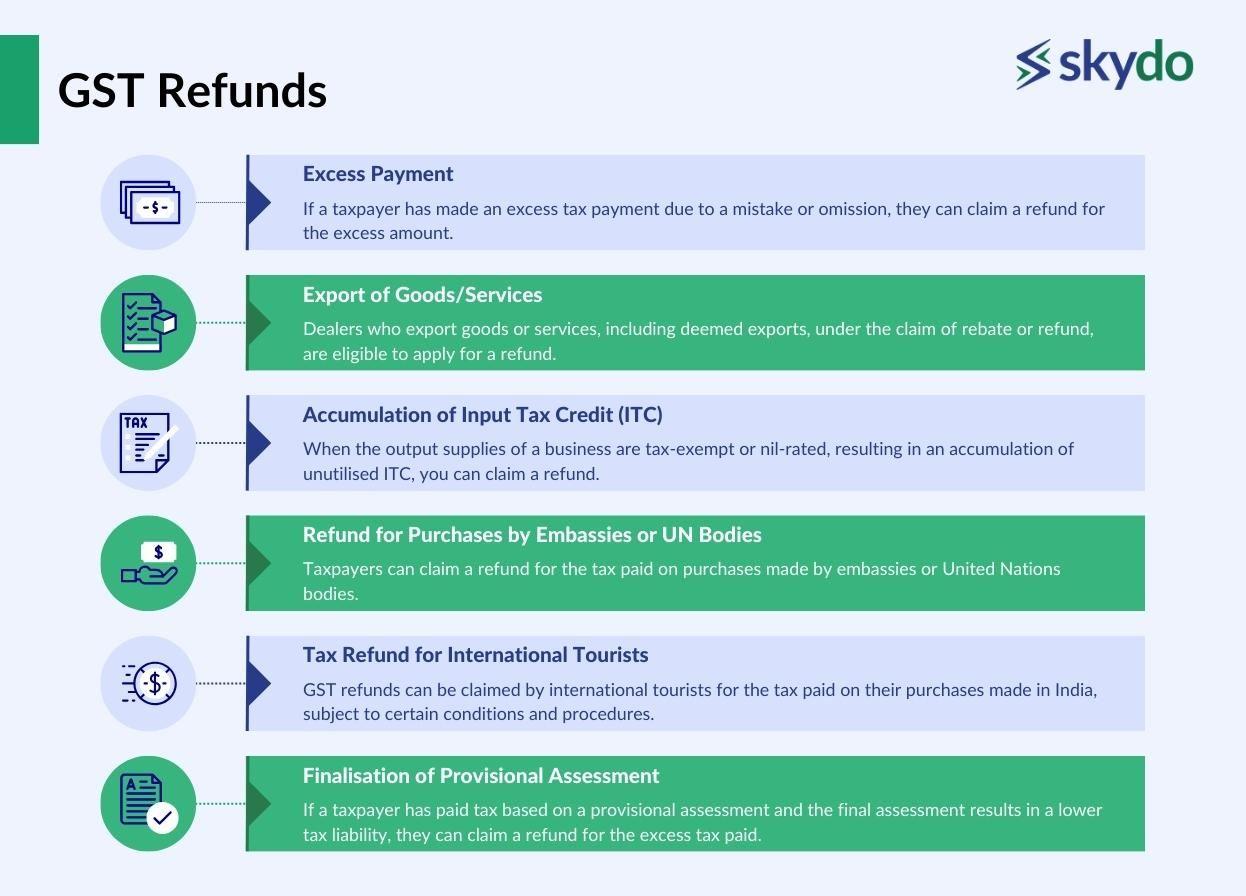
- Excess Payment: If a taxpayer has made an excess tax payment due to a mistake or omission, they can claim a refund for the excess amount.
- Export of Goods/Services: Dealers who export goods or services, including deemed exports, under the claim of rebate or refund, are eligible to apply for a refund.
- Accumulation of Input Tax Credit (ITC): When the output supplies of a business are tax-exempt or nil-rated, resulting in an accumulation of unutilised ITC, you can claim a refund.
- Refund for Purchases by Embassies or UN Bodies: Taxpayers can claim a refund for the tax paid on purchases made by embassies or United Nations bodies.
- Tax Refund for International Tourists: GST refunds can be claimed by international tourists for the tax paid on their purchases made in India, subject to certain conditions and procedures.
- Finalisation of Provisional Assessment: If a taxpayer has paid tax based on a provisional assessment and the final assessment results in a lower tax liability, they can claim a refund for the excess tax paid.
Calculating and Claiming GST Refunds
You must determine the amount of excess tax paid or the eligible refundable amount based on specific circumstances to claim a refund. You should submit the refund application within the prescribed time limit.
Here's the step-by-step process for claiming a GST refund.
- Duly fill out Form RFD-01 with all the necessary details.
- Attach supporting and relevant documents to substantiate the claim, such as invoices, export documents, etc.
- In some cases, the refund application needs to be certified by a Chartered Accountant or competent authority as specified by the GST laws.
- The refund application should be filed electronically through the GST portal within the prescribed time limit.
- Once the refund application is filed, it is processed by the tax authorities. They may scrutinise the application and supporting documents before approving the refund.
- If the refund claim is eligible and correct, the refund amount is credited to your business’ bank account through the Electronic Cash Ledger.
You can reach out to Skydo for any queries you may have about GST compliance for your export service business. Visit our website or contact our customer support team to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on GSTIN and Export Business
Q1. What is GST?
Ans: GST, or Goods and Services Tax, is a unified indirect tax system implemented in India. It replaces multiple taxes like VAT, excise duty, and service tax, simplifying the tax structure. GST is levied at various stages of the supply chain, from manufacturing to consumption, and is based on the value addition principle. It helps streamline tax collection, reduce tax evasion, and promote a more efficient and transparent taxation system.
Q2. Can unregistered businesses engage in export services?
Ans: No, unregistered businesses cannot engage in exports. Every exporter must register under GST and obtain a GSTIN.
Q3. What is the procedure for obtaining a GSTIN for export service businesses?
Ans: Business owners must apply for GST registration through the GST Portal and provide their business details, PAN, and other relevant documents.
Q4. How does GST affect the pricing of export services?
Ans: Business owners can claim input tax benefits on GST paid for purchases. It reduces the tax burden and makes them more competitive internationally.
Q5. What happens if an exporter fails to comply with GST regulations?
Ans: If an exporter fails to comply with GST regulations, they may face fines, cancellation of registration, penalties and other legal consequences.