10 International Payment Terminologies Every Service Exporter Must Know

One of the main challenges businesses face when exporting services globally is navigating international payments. Different countries have different export payment terms, payment systems, currencies, and regulations, making it difficult for businesses to know which payment method to use, how to negotiate payment terms and manage exchange rate risk.
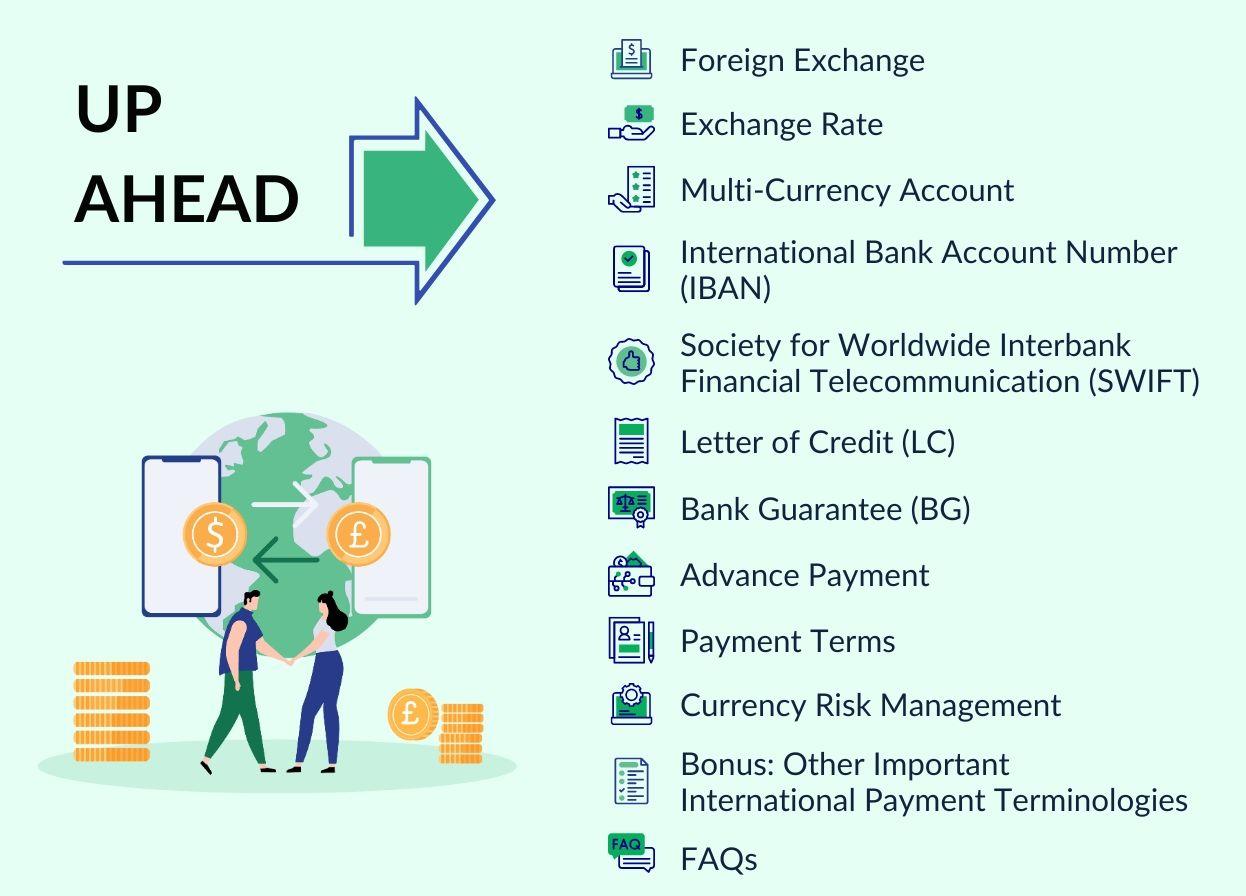
Understanding payment terms in export is essential for businesses that export services globally. Here are ten important international payment terminologies for global export business:
#1: Foreign Exchange (Forex or FX)
Forex, or foreign exchange, refers to the global marketplace for trading national currencies against one another. It plays a pivotal role in international trade by facilitating the conversion of currencies and enabling businesses to engage in cross-border transactions.
Understanding the Forex market is crucial for businesses as it allows them to manage currency risks, hedge against exchange rate fluctuations, and optimize pricing strategies.
A nuanced comprehension of Forex dynamics allows businesses to strategically hedge against currency volatility, ensuring stable profit margins and fostering competitive advantages in the ever-evolving landscape of international trade. In essence, mastery of Forex enhances financial resilience, fostering a more agile and adaptive approach to global business.
#2: Exchange Rate
Exchange rates represent the value of one currency in terms of another, determining the cost of international transactions. Fluctuations in exchange rates significantly impact your international payments, affecting the amount you receive or pay.
Influencing factors of exchange rate fluctuations include–
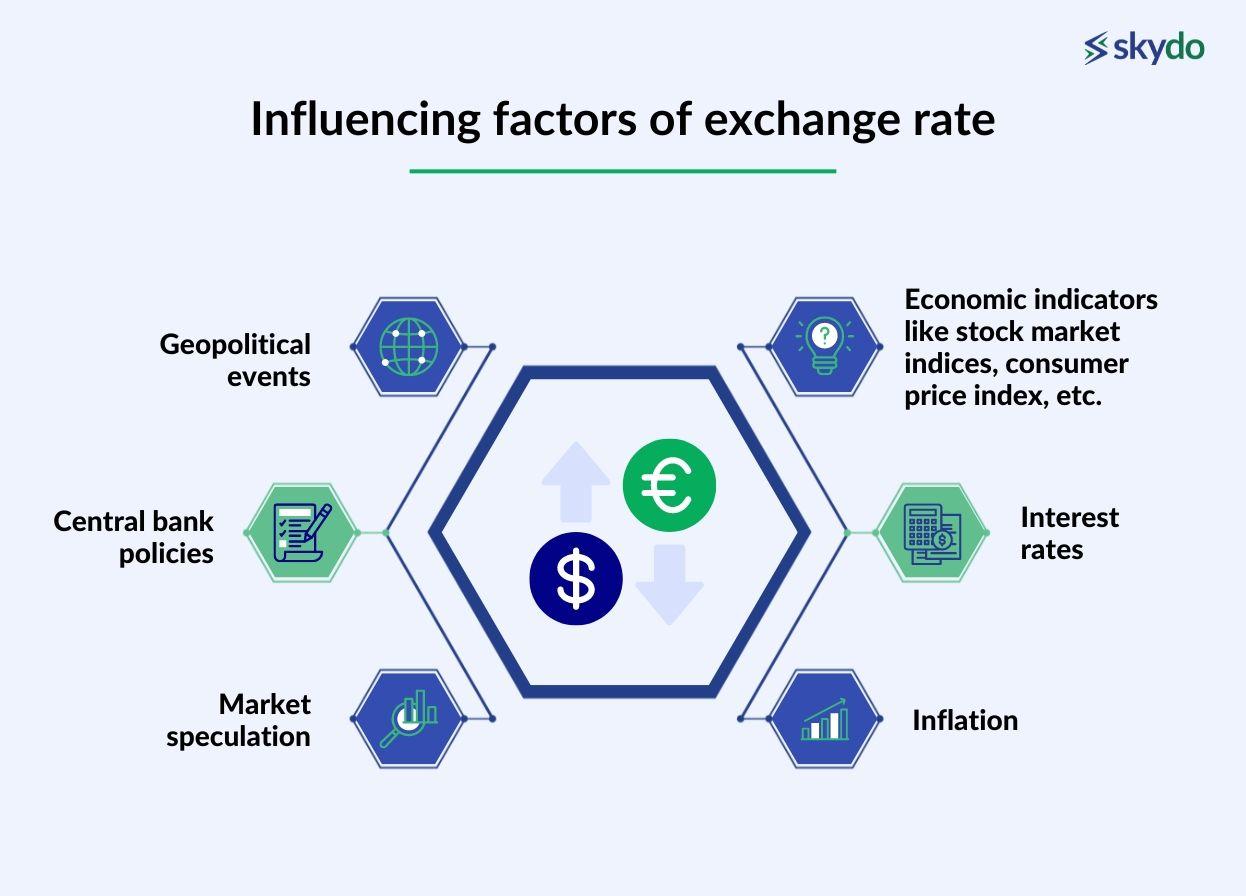
- Economic indicators like stock market indices, consumer price index, etc.
- Interest rates
- Inflation
- Geopolitical events
- Central bank policies
- Market speculation
Monitoring these factors is crucial for individuals and businesses engaged in cross-border transactions, as understanding exchange rate dynamics helps mitigate risks and optimize financial decisions, ensuring your international payment methods align with prevailing market conditions.
#3: Multi-Currency Account
A multi-currency account is a versatile financial ally in international payment methods that empowers you to hold and manage funds in various currencies within a single account. With this account, you can seamlessly transact and keep money in different currencies, offering flexibility and convenience in international dealings.
Its features include real-time currency exchange, enabling you to switch between currencies at competitive rates. In addition, having a multi-currency account can reduce fees when conducting transactions in foreign currencies.
#4: International Bank Account Number (IBAN)
The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is a globally recognised identifier for bank accounts. In your international transactions, IBANs play a crucial role in simplifying and securing cross-border payments. They ensure accuracy by providing a standardised format, reducing errors in manual data entry.
With IBANs, transactions become more efficient, as they contain essential information like the country code and account number. This streamlines the process and enhances security by preventing misrouting of funds.
Let’s take an example of an IBAN for a hypothetical bank in the US.
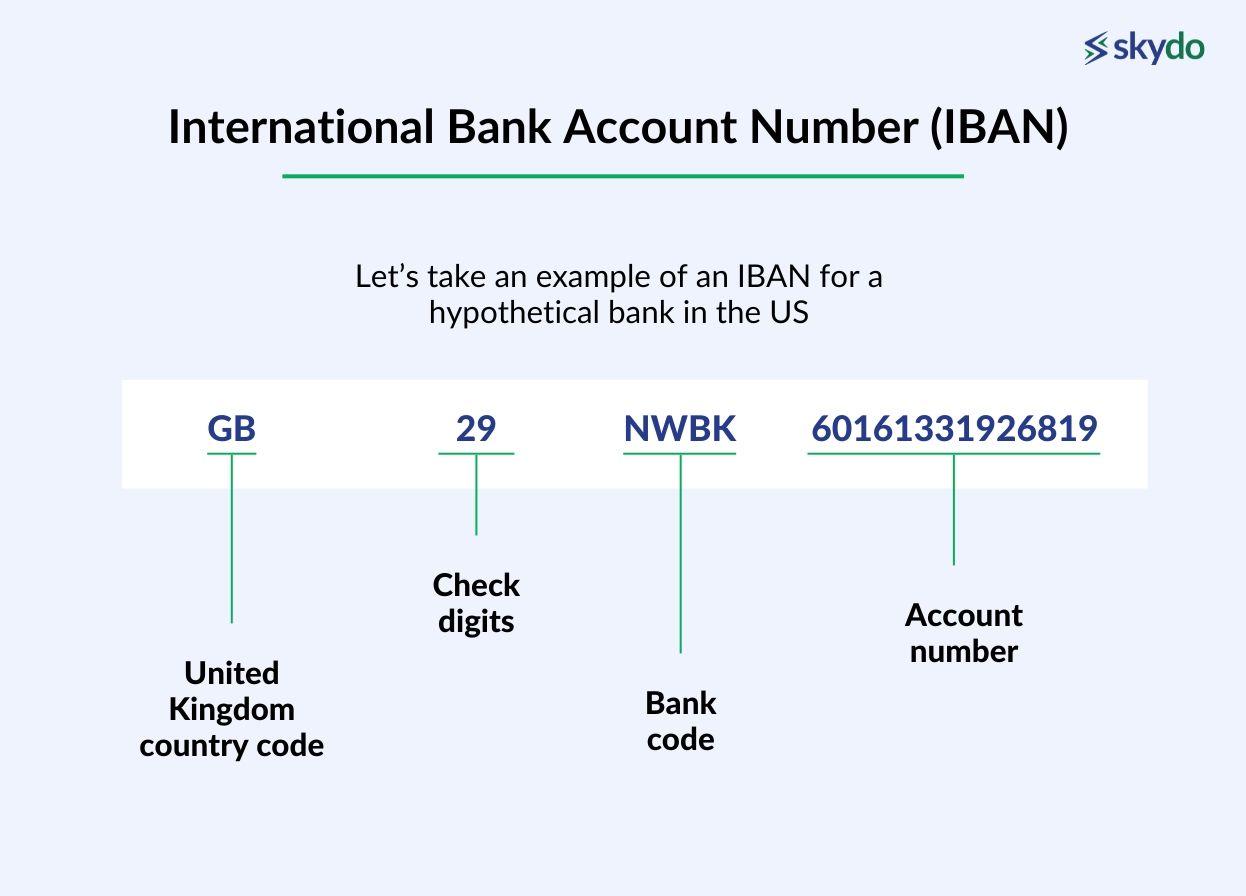
The IBAN would be GB29NWBK60161331926819.
"GB" represents the country code (United Kingdom).
"29" is the check digits.
"NWBK" is the bank code.
"60161331926819" is the account number.
#5: Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT)
Entrusting your global financial transactions to the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) is a strategic move in international finance.
SWIFT operates as a member-owned cooperative, providing a secure messaging network that facilitates seamless money transfers between participating banks. Its role in international transactions is pivotal, acting as the linchpin for secure communication among financial institutions worldwide.
Central to the efficacy of SWIFT is the utilisation of unique codes, commonly known as SWIFT codes or bank identifier codes (BIC). These codes, typically eight or 11 characters long, play a crucial role in ensuring the security and efficiency of payments.
For instance, the Italian bank UniCredit Banca boasts the SWIFT code UNCRITMM, where each segment holds specific information about the institution, its country, and its location.
SWIFT codes serve as digital fingerprints, guaranteeing that funds reach their intended destination with precision. The meticulous encoding of sender and recipient information within these codes expedites transactions and fortifies the financial ecosystem against potential security threats.
In essence, SWIFT and its codes are guardians of the global financial landscape, enabling you to navigate cross-border transactions with confidence and reliability.
#6: Letter of Credit (LC)
A Letter of Credit (LC) serves as a financial lifeline, defining a predetermined line of credit for international transactions. This crucial instrument assures payment, mitigating risks inherent in cross-border deals. Acting as a contractual guarantee, LCs boost trust between you and clients by ensuring funds are set aside for payment upon service delivery.
This secure payment method establishes a framework for seamless transactions, fostering a reliable and transparent relationship with partners worldwide. As the backbone of your payment system, LCs not only define financial parameters but also fortify the foundation of trust in the dynamic landscape of global IT services.
#7: Bank Guarantee (BG)
Embracing bank guarantees (BGs) for payment acceptance is pivotal in your global IT service business. BGs serve as a financial safety net, ensuring secure transactions on an international scale.
Functioning as a commitment from a bank that payment will be made in the event of a default, BGs offer reassurance to both parties involved. For your business, this means guaranteed payment upon successful service delivery, fostering trust and mitigating risks associated with cross-border transactions.
#8: Advance Payment
Advance payments in international trade refer to funds transferred by the buyer to the seller before the goods or services are delivered. This prepayment is a common method to secure a transaction, providing the seller with financial assurance.
One advantage for businesses using advance payments is immediate cash flow, aiding in production or procurement. However, the buyer faces the risk of non-delivery or dissatisfaction, making due diligence crucial.
Documentary collection, an alternative, involves a bank facilitating the exchange of documents for payment. Its purpose is to reduce payment risks while offering flexibility. Unlike letters of credit, documentary collection does not provide the same level of security, but it is less costly and complex.
While advance payments offer quick liquidity, they may strain buyer-seller relationships due to trust concerns. The documentary collection strikes a balance between security and simplicity.
Understanding these methods is vital for businesses engaged in global transactions, allowing them to choose the most suitable payment mechanism based on their specific needs and risk tolerance.
#9: Payment Terms
Selecting appropriate payment terms is crucial for international trade. Understand the common options to make informed decisions tailored to your business needs. Among the widely used terms is Letter of Credit (L/C), where a bank guarantees payment upon compliance with agreed-upon conditions.
Advance Payment demands payment before shipment, providing security but potentially affecting buyer trust. Open Account involves trust between parties, with the seller shipping goods before payment. To strike a balance, consider Cash in Advance for security or Open Account for established relationships.
For your business, assess factors such as cash flow, risk tolerance, and relationship history with your global clients. Balance the buyer's need for credit against your desire for payment security.
Building a comprehensive understanding of terms of payment in export ensures smoother transactions, reduces financial risks, and fosters stronger international business relationships. Tailor your approach, considering the unique dynamics of your industry and partners, to make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
#10: Currency Risk Management
Currency risk in global transactions refers to the potential financial loss due to fluctuating exchange rates. When conducting international business, changes in currency values can impact profits and expenses.
To shield your business, employ strategic currency risk management. Hedge against volatility using financial instruments like forward contracts or options, fixing exchange rates in advance. Diversify currency holdings to spread risk, minimising the impact of adverse movements.
Stay informed about geopolitical events and economic indicators influencing currency markets. By adopting these strategies, you'll fortify your business against currency risk, ensuring stability in an unpredictable global financial landscape.
Bonus: Other Important International Payment Terminologies

- FIRC - FIRC stands for Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate. It is a document issued by banks in India to confirm the receipt of payment from a foreign source for inward remittance transactions.
- Spot rate - The exchange rate at which two currencies can be converted immediately.
- Payment gateway - A service that securely processes online transactions and facilitates communication between the merchant, customer, and financial institutions.
- Forward rate - The exchange rate at which two currencies can be converted at a future date.
- Hedging - A risk management strategy used to protect against fluctuations in exchange rates.
- Transaction fees - Fees charged by banks or financial institutions for processing transactions.
- Conversion fees - Fees charged for converting one currency to another.
- Correspondent bank fees - Fees charged by intermediary banks when processing international payments.
- Foreign exchange risk - The risk of losses due to changes in exchange rates between currencies.
- Chargeback - A dispute between a customer and a merchant over a payment that results in the funds being returned to the customer.
- Swift code - A unique code used to identify banks and financial institutions in international transactions.
- Wire transfer - A method of electronically transferring funds between banks or financial institutions.

Final Words
Comprehending international payment terminologies is paramount for businesses venturing into global service exports. Mastery of payment regulations language ensures avoidance of legal and financial pitfalls, fostering a seamless cross-border transaction experience.
Staying abreast of evolving global payment trends is indispensable for maintaining a competitive edge. By navigating the intricate landscape of international payments, businesses position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks. A nuanced understanding of these terminologies not only safeguards against pitfalls but also establishes a foundation for successful and compliant global business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the methods of payment in international trade?
Ans: International trade commonly involves payment methods such as letters of credit, bank transfers, and open account transactions. These methods ensure secure and efficient cross-border transactions.
Q2. What are the common methods of foreign payments?
Ans: Common methods of international payment include letters of credit, bank transfers, and open account transactions. These foreign payment methods facilitate smooth and secure financial transactions between parties engaged in global trade.
Q3. What is documentary credit?
Ans: Documentary credit or letter of credit is a financial arrangement widely used in international trade, issued by a bank to guarantee payment to the seller upon the fulfilment of specified conditions.
Q4. What is a documentary collection?
Ans: Documentary collection is a method of payment in international trade where a seller entrusts the handling of shipping documents to banks, with the buyer making payment upon document presentation as per agreed terms.