RBI’s PACB Circular: OPGSP Update 2024

On October 31, 2023, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a master circular on the import of goods and services titled Regulation of Payment Aggregator – Cross Border.
According to the circular, the RBI will regulate all Indian entities facilitating online cross-border payments for the import and export of permissible goods and services. Moreover, these entities will be collectively termed Payment Aggregators Cross Border (PA-CB).
The circular comprises guidelines to streamline the existing cross-border payment framework in India. Previously, cross-border transactions were carried out through Online Payment Gateway Service Providers (OPGSPs) as per a circular issued by RBI in 2015.
OPGSPs operate by partnering with an Authorised Dealer (Category I) Bank (AD Bank) and notifying the RBI. According to RBI guidelines, no formal license is needed to function as an OPGSP.
Hence, RBI has issued a circular to establish a concise and clear framework for cross-border payments. RBI will now oversee all cross-border payments in India related to the import and export of goods. The circular applies to PA-CB, PAs, authorised banks and OPGSPs. The PA-CB circular also denotes that there can’t be any new OPGSP.
This blog discusses the key provisions related to the latest RBI circular on the import of goods and services, RBI guidelines for payment gateway, and OPGSP guidelines.
Master Circular on Import of Goods and Services: RBI Bank Guidelines
The following are the key guidelines mentioned in the circular.
1. Applicability
The following entities need to adhere to RBI guidelines/instructions provided in the circular.
- Entities
All entities, including authorised dealer banks and non-banks, involved in settling/processing cross-border transactions. The cross-border transactions must be for importing and exporting goods and services, and the transaction must be executed online (digitally). - PA-CBs
Under the new circular, these non-bank entities are referred to as Payment Aggregator-Cross Border (PA-CB).
2. Key Developments
Here are the key developments included in the new PACB circular.
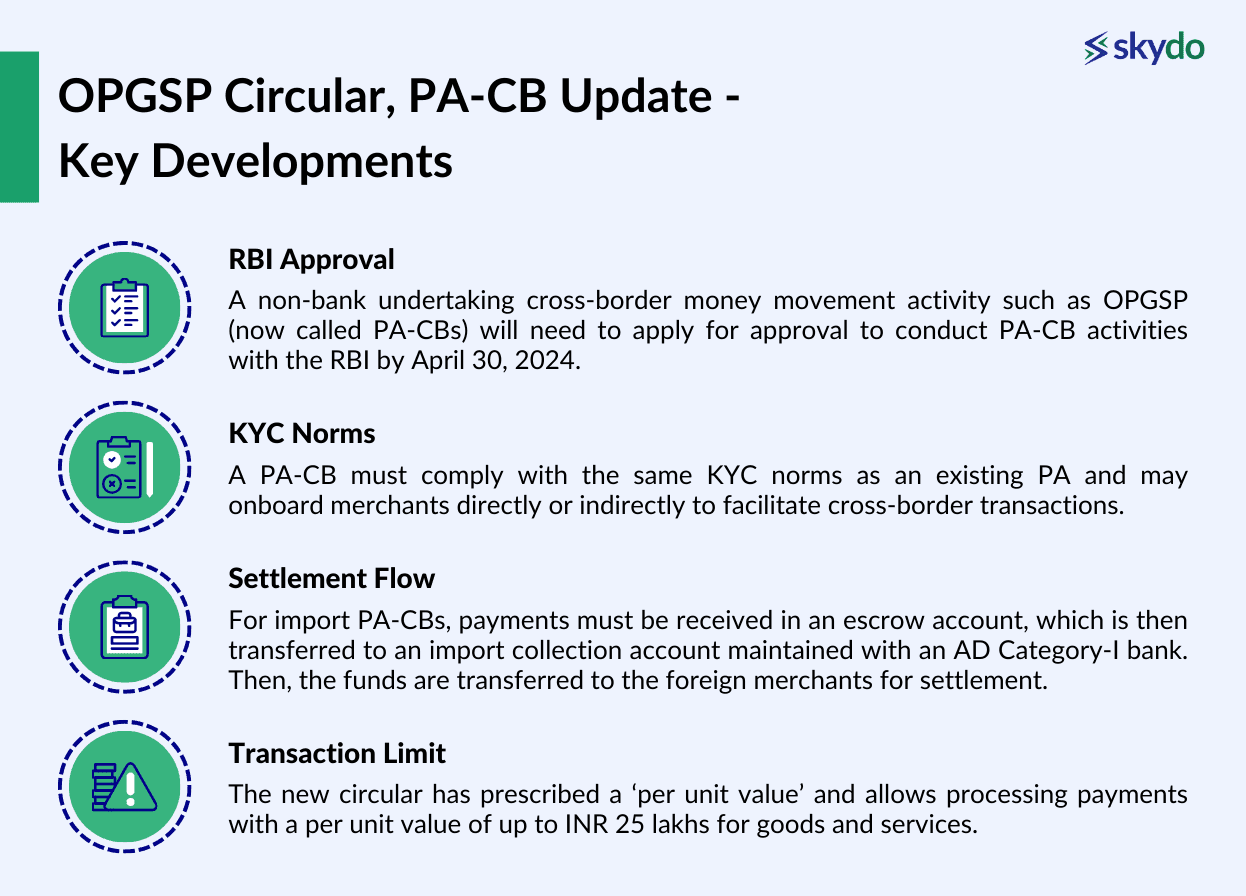
- RBI Approval
A non-bank undertaking cross-border money movement activity such as OPGSP (now called PA-CBs) will need to apply for approval to conduct PA-CB activities with the RBI by April 30, 2024. PA-CBs must also register with the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND) before applying for approval with the RBI.
Furthermore, a non-bank existing PA (payment aggregator) must inform the RBI about its existing PA-CB activity and if it intends to continue such activities within 60 days from the circular date.
- KYC Norms
Domestic PAs can perform KYC procedures as per a board-approved policy, However, PA-CBs must comply with the KYC norms mentioned in the Master Direction on KYC.
Furthermore, the PA-CBs need to undertake due diligence of the buyer if the per unit value of goods/services imported exceeds INR 2.5 lakhs.
- Settlement Flow
For import PA-CBs, payments must be received in an escrow account, which is then transferred to an import collection account maintained with an AD Category-I bank. Then, the funds are transferred to the foreign merchants for settlement.
For export PA-CBs, payments must be received by maintaining multiple export collection accounts for each currency with AD Category-I bank. The PA-CBs can settle in non-INR currencies for directly onboarded merchants.
Import and export PA-CBs must comply with guidelines specified for both import and export flows by maintaining separate import and export collection accounts with AD Category-I banks. The permitted debits and credits are the same as for a PA.
- Transaction Limit
The new circular has prescribed a ‘per unit value’ and allows processing payments with a per unit value of up to INR 25 lakhs for goods and services.
Categories of Authorisation as per PA-CB Activity
Based on the cross-border payment activity undertaken by the PA-CBs, they can seek authorisation for one of the following three categories.
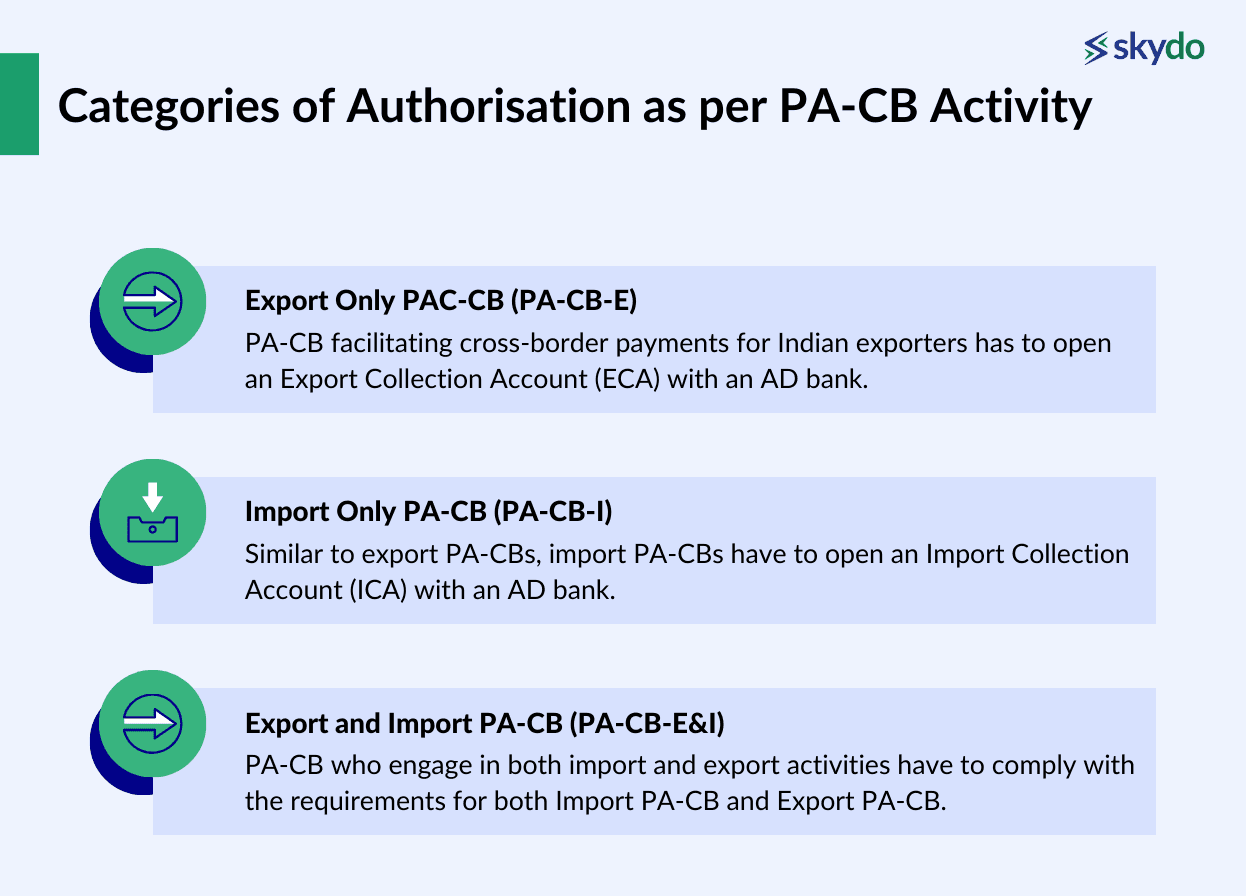
- Export Only PAC-CB (PA-CB-E)
- Import Only PA-CB (PA-CB-I)
- Export and Import PA-CB (PA-CB-E&I)
1. Export Only (PA-CB-E)
PA-CB, facilitating cross-border payments for Indian exporters, has to open an Export Collection Account (ECA) with an AD bank.
ECAs can be opened in either Indian currency or foreign currency. In the case of the latter, various ECAs have to be opened for different currencies.
The PA-CBs will credit all export proceeds in the respective ECAs. Additionally, export PA-CBs need to follow the below guidelines:
- Ensure all goods and services exported are permitted as per the Foreign Trade Policy
- Perform diligence on merchants, e-commerce marketplaces, and payment aggregators
2. Import Only (PA-CB-I)
Similar to export PA-CBs, import PA-CBs have to open an Import Collection Account (ICA) with an AD bank.
They will collect the payment from importers in an escrow account managed by the payment aggregator. It will then be transferred to ICA and will eventually be transferred to the bank account of the foreign merchants.
These entities are allowed to directly onboard foreign merchants, e-commerce marketplaces, or other overseas entities that offer payment aggregation services.
Here are the guidelines Import PA-CBs need to follow.
- Ensure India's Foreign Trade Policy does not prohibit the import of such goods or services
- Onboard overseas merchants as per RBI’s KYC Master Directions
- If the per unit cost of imported goods or services is more than ₹2,50,000, the Importer PA-CB will also do diligence of the importer as per KYC Master Directions
3. Export and Import (PA-CB-E&I)
Those PA-CB who engage in both import and export activities have to comply with the requirements for both Import PA-CB and Export PA-CB.
They also need to ensure that the maximum value per unit of exported or imported goods or services should be ₹25,00,000.
Net-Worth Requirement for Non-Bank PA-CB
Non-banks who want to provide PA-CB services will have to seek authorisation from RBI. However, before seeking RBI authorisation, it is necessary to register with the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND).
However, RBI has issued the following net-worth criteria for non-banks providing PA-CB services.
| Entity | Minimum Networth (in ₹) | Due Date | Additional Requirement to Verify Networth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Border Existing PA-CBs | 15 crore to 25 crore | At the time of applying to RBI to gain authorisation By March 31, 2026 | 1. Certificate from statutory auditor 2. Audited statements of the latest financial accounts |
| Newly incorporated non-bank PA-CBs | 15 crore to 25 crore | At the time of applying to RBI to gain authorisation By the end of the third financial year from the date of grant of authorisation | 1. Certificate from statutory auditor evidencing net worth2. Provisional balance sheet |
The accounts of existing non-bank PA-CB who are unable to meet the net worth requirement will be closed by banks by 31 July 2024.
Snapshot Comparison Between OPGSP Circular (2015) and PA-CB Circular (2023)
Here are the key differences between the OPGSP Circular (2015) and the PA-CB Circular (2023)
| Regulatory Requirements | OPGSP Circular (2015) | PA-CB Circular (2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Required to obtain RBI authorisation | RBI authorisation is not needed. However, they were required to have a standing agreement with AD Category I banks to ensure compliance with RBI requirements. | Non-banks PA-CBs: Required to seek approval from RBI by April 30, 2024.AD Category-I banks: Not required to seek RBI approval. |
| Net Worth Requirements | Not needed | PA-CBs must have a net worth of INR 15 crores at the time of application.Their net must increase to INR 25 crores by March 31, 2026. |
| Transaction Limits | Capped aggregate translation value:Import: USD 2,000Export: USD 10,000 | Capped per-unit transaction limit of goods and services:INR 25 lakhs |
| Nature of allowed transactions | Imports: goods and softwareExports: goods and services (as permitted under India’s foreign trade policy). | Import and export of all the goods and services as permitted under India’s foreign trade policy. |
| KYC Norms | Must follow appropriate KYC norms while onboarding merchants directly or indirectly. | Must follow KYC checks as per RBI’s master directions before onboarding merchants directly or indirectly. Further, they must undertake KYC checks of a buyer if the per-unit transaction value exceeds INR 2.5 lakhs. |
| Technology standards | Compulsory adhering to the IT ACT, 2000, and all other applicable regulations. | PA-CBs must comply with technology recommendations listed in the RBI’s PA-PG guidelines released on March 17, 2020. |
The License Application Process
Here is the process of seeking approval from RBI for existing or new PA-CBs.
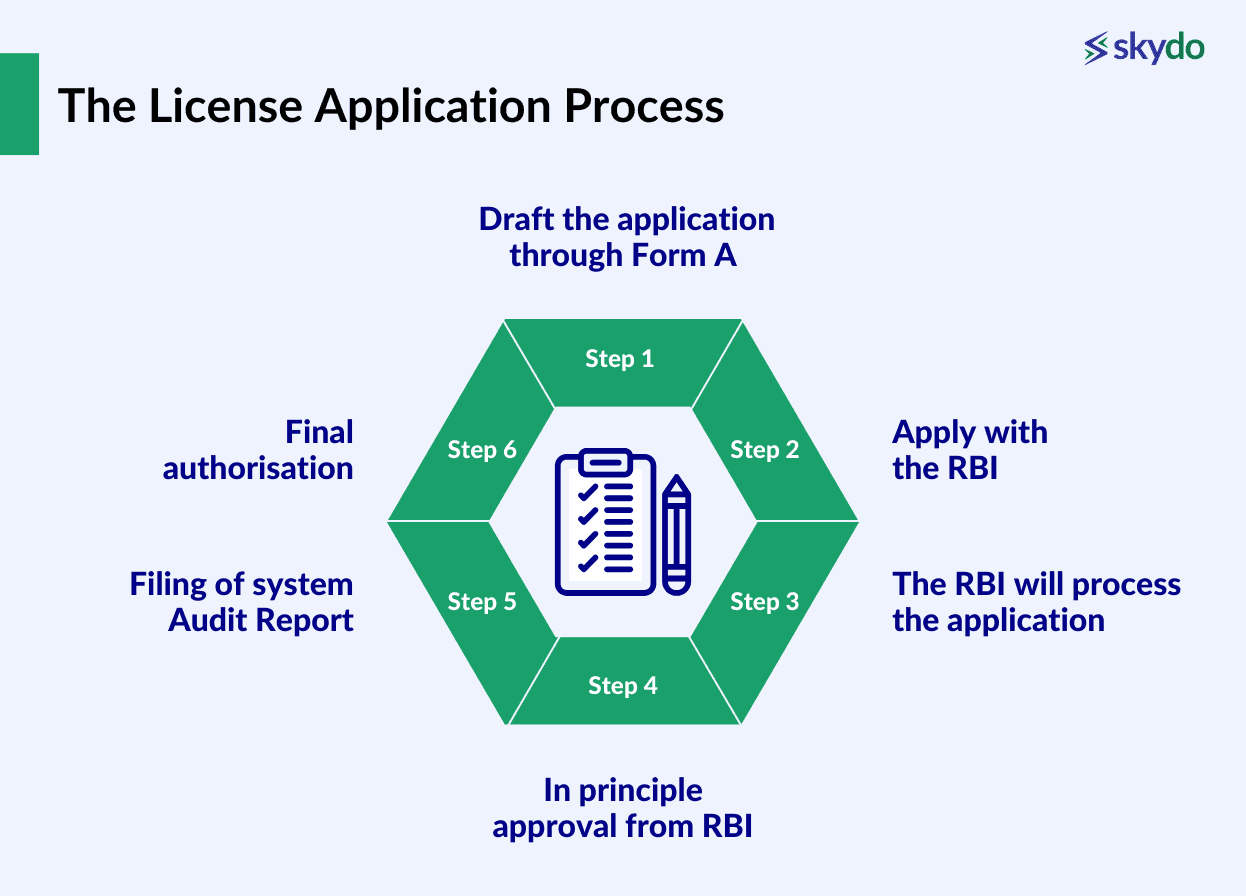
Step 1: Draft the application through Form A, which includes the following parts.
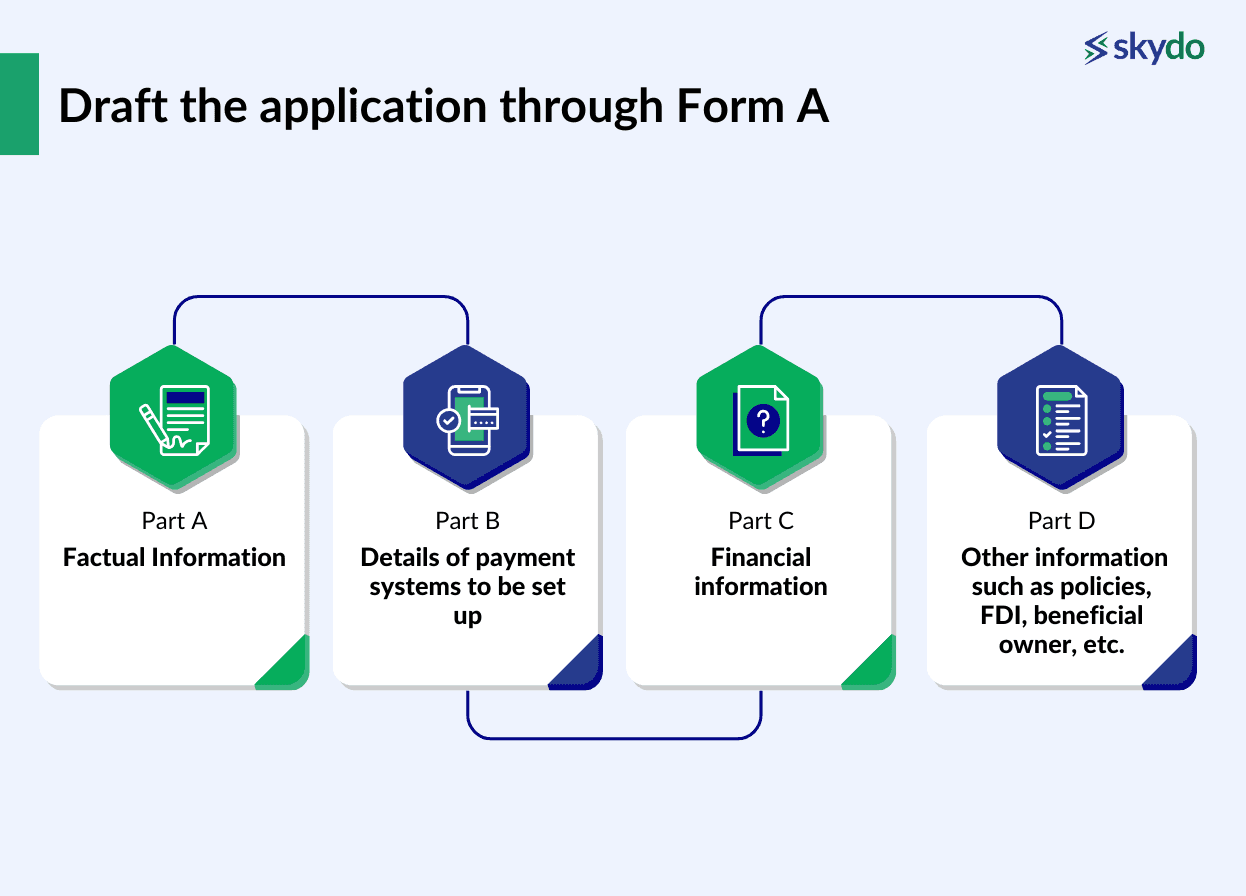
- Part A: Factual Information
- Part B: Details of payment systems to be set up
- Part C: Financial information.
- Part D: Other information such as policies, FDI, beneficial owner, etc.)
Step 2: Apply with the RBI.
Step 3: The RBI will process the application.
(RBI may raise queries related to various aspects such as shareholding, product processes, etc.)
Step 4: In principle approval from RBI.
(validity period of six months)
Step 5: Filing of system Audit Report
(RBI may raise queries related to SAR audit observations)
Step 6: Final authorisation(state additional conditions that must be complied with)
Conclusion
The evolving cross-border payments environment and the emergence of several OPGSPs and other fintech entities encouraged RBI to issue the circular. Its main purpose is to ensure seamless and more transparent cross-border payment transactions.
Even though regulatory authorities are constantly working on making cross-border payment transactions seamless, transparent, secure, and quicker, businesses often face difficulties in receiving timely payments.
Skydo aims to simplify the cross-border payment landscape for businesses by automating various tasks and helping businesses open foreign bank accounts. Join Skydo today to streamline your invoicing and financial management activities!
FAQs
Q1. RBI’s master circular on the import of goods and services and cross-border payments applies to which entities?
Ans. AD banks, PAs, and PA-CBs involved in the online processing/settlement of cross-border payment transactions related to the import and export of goods and services have to comply with the guidelines mentioned in the circular.
Q2. What are various compliances according to RBI payment aggregator guidelines for cross-border payments?
Ans. All PA-CBs have to follow the guidelines provided in the circular dated October 31, 2023. Additionally, they also have to follow the various guidelines for payment aggregators mentioned under a circular issued by RBI on March 17, 2020. The circular includes guidelines related to customer grievance redressal and compliance with Baseline Technology Guidelines to ensure fraud prevention and risk management.
Q3. How can PA-CB seek authorisation for facilitating cross-border payment transactions?
Ans. AD banks do not need to seek authorisation to facilitate cross-border payment transactions. However, a non-bank PA-CB can seek authorisation from RBI by sending the application to the Department of Payment and Settlement Systems (DPSS), RBI, Central Office (CO), by April 30, 2024. PA-CB entities must fulfil the minimum net worth criteria before applying to RBI.