Professional Tax for Freelancers in 2024

Professional Tax is governed and levied by the respective state governments' professional tax acts. The amount you owe in taxes varies based on factors such as income, the nature of the profession, and the state in which the individual operates.
Here is everything you need to know about PT as a freelancer.
What is Professional Tax?
If a person is salaried, the employers are responsible for deducting the professional tax amount directly from the salary. However, the government requires professionals such as freelancers to pay the P tax directly to their state government. Professional tax meaning is not based on income but rather on the nature of the profession or employment. It is meant to contribute to the state's revenue and development. The professional tax differs from other types of taxes mentioned below.
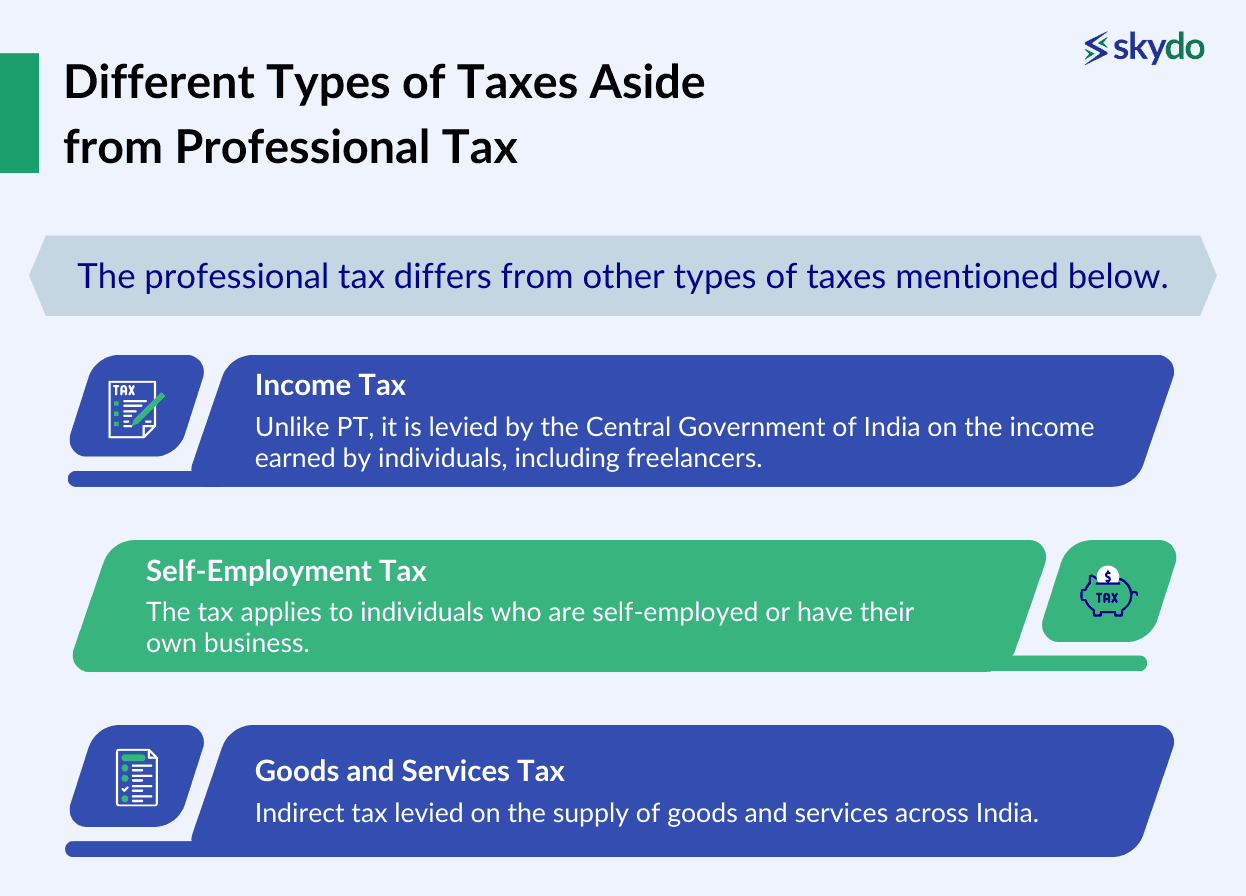
- Income Tax
Unlike PT, it is levied by the Central Government of India on the income earned by individuals, including freelancers.
- Self-Employment Tax
The tax applies to individuals who are self-employed or have their own business.
- Goods and Services Tax
Indirect tax is levied on the supply of goods and services across India.
Here is the basic structure of professional tax in India.
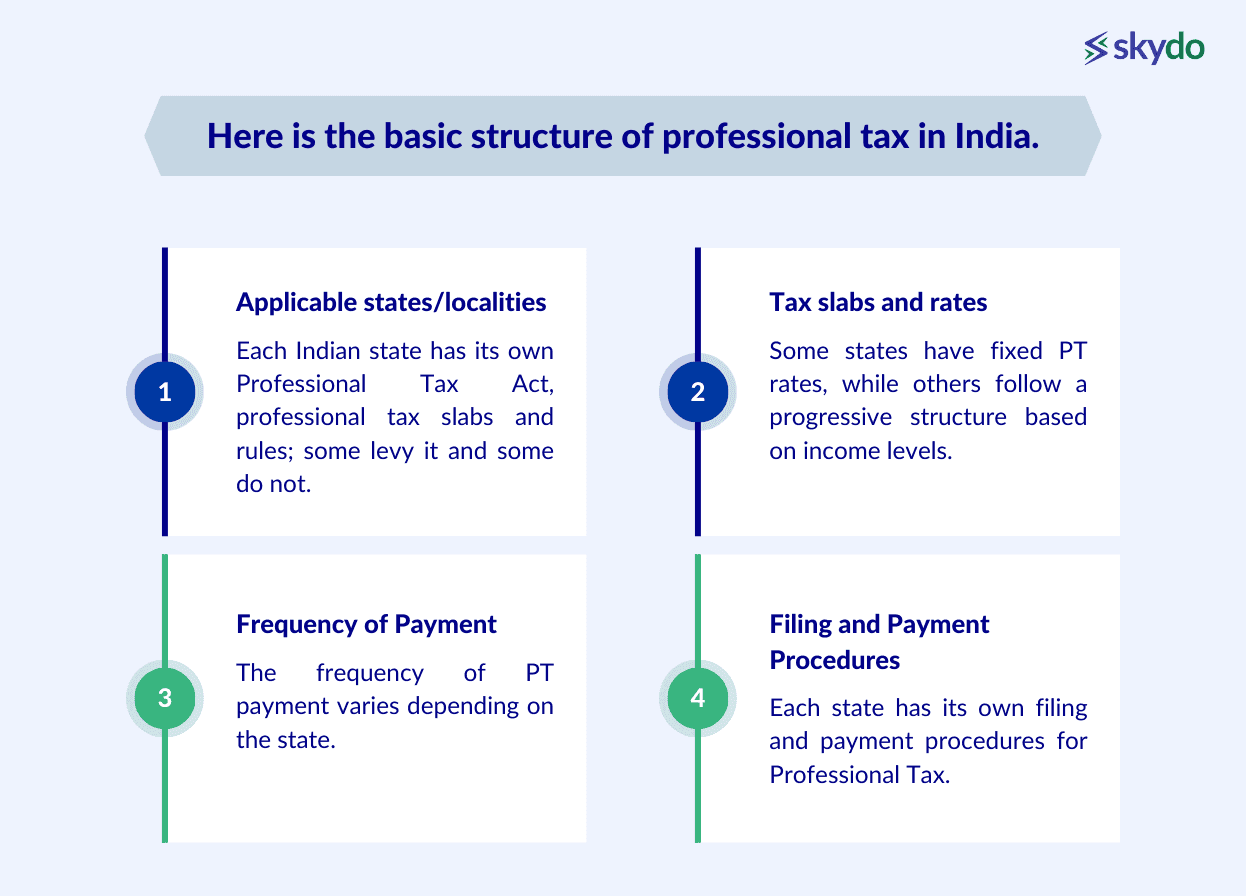
- Applicable states/localities
Each Indian state has its own Professional Tax Act, professional tax slabs and rules; some levy it, and some do not. Some states have municipalities that levy their own PT in addition to the state tax. It is wise to check with your local authority regarding the applicable professional tax.
- Tax slabs and rates
Some states have fixed PT rates, while others follow a progressive structure based on income levels. For example, Maharashtra has different slabs for men, women, and senior citizens for gross salaries starting from Rs 7,500 to Rs 25,000.
- Frequency of Payment
The frequency of PT payment varies depending on the state. It can be monthly, quarterly, or yearly. For example, Rajasthan allows paying the tax annually or monthly.
- Filing and Payment Procedures
Each state has its own filing and payment procedures for Professional Tax. This often involves registering with the local tax authorities, obtaining a registration certificate, and filing regular returns through online portals or designated offices.
Calculate your Professional Tax Liability
Professional tax liability depends on a freelancer's state of operations and earnings. However, irrespective of these two factors, the professional tax limit is Rs 2,500 for a month.
Here is the process of how to calculate professional tax on salary or earnings.

Minimise your Professional Tax Burden
To minimise your professional tax burden as a freelancer, leverage deductions and exemptions available in your location. Here are some deductions and exemptions that freelancers can utilise:
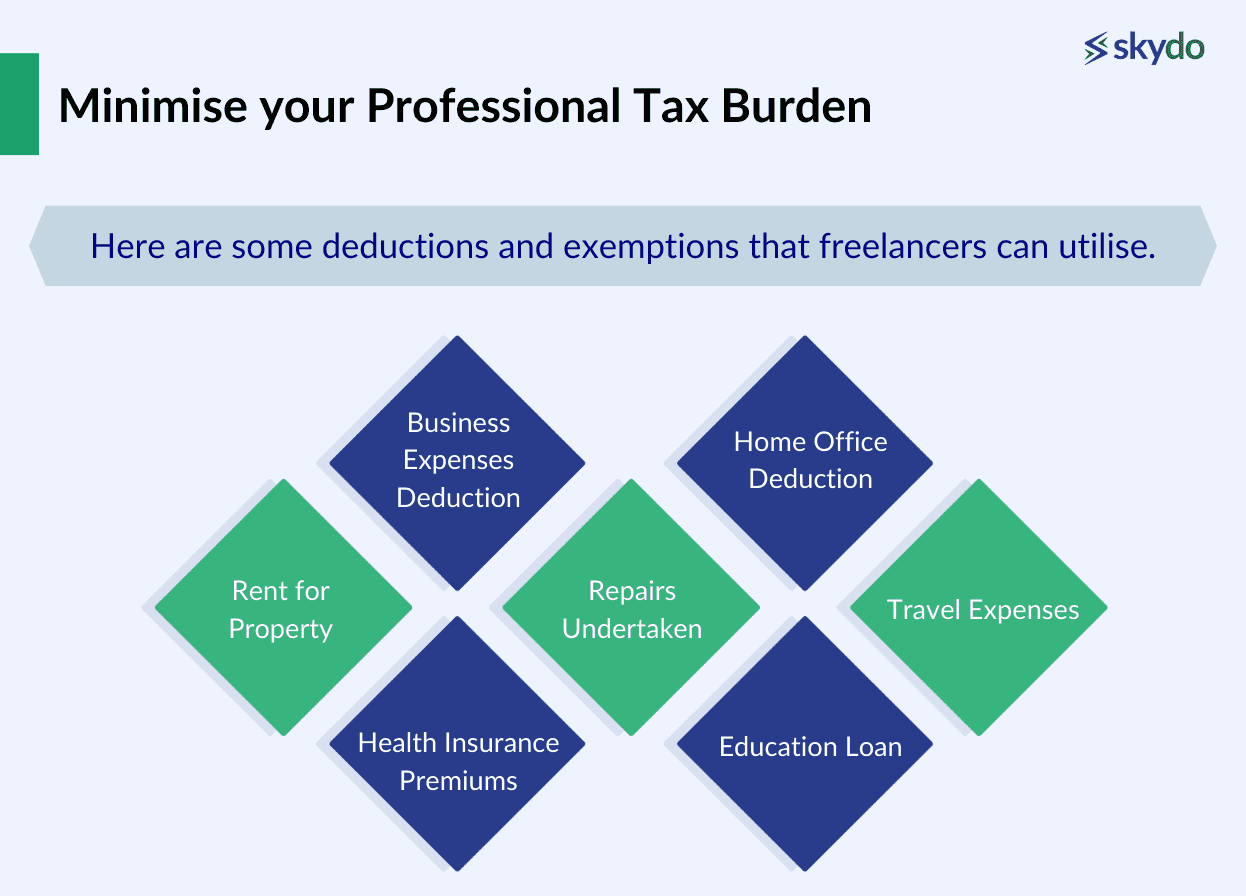
- Business Expenses Deduction
- Home Office Deduction
- Rent for Property
- Repairs Undertaken
- Travel Expenses
- Health Insurance Premiums
- Education Loan
You can use various accounting software or apps, such as Khatabook, Open Money, TallyPrime, etc., to keep track of your expenses. Furthermore, it is wise to regularly reconcile your financial records to ensure accuracy and identify potential deductible expenses.
Additional Considerations
Certain freelance professions or industries may be subject to specific taxes or regulations beyond professional tax and income tax. For example, online content creators, such as bloggers, YouTubers, and influencers, may need to comply with digital services taxes or regulations specific to online advertising revenue.
Hence, consulting a tax advisor or researching extensively is important to know your compliance and taxation liabilities. You may also have to register for GST if your annual income from freelancing is above Rs 20 lakh.
Conclusion
Proactively managing your professional tax obligations as a freelancer can minimise tax burdens and avoid potential penalties or legal issues. Moreover, seeking professional advice from tax consultants or accountants can provide invaluable guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
For further resources on freelancing, you can read Skydo’s blogs and open a free virtual currency account if you receive foreign remittances.
Q1. What is the new tax rule for 2023-2024?
Ans: The new tax rule states that the tax exemption limit is Rs 2,50,000 for individuals, NRIs, and HUFs below 60 years of age.
Q2. Do freelancers have to pay professional tax?
Q3. Which ITR is applicable for freelancers?
Q4. How do I claim my TDS refund as a freelancer?
Q5. Why is professional tax deducted?