PSD2 and its Impact on International Payments

It all began in 2007 when the European Union launched a directive that majorly streamlined cross-border transactions within the European Economic Area (EEA). The directive called the Payment Service Providers Directive (PSD), aimed to develop a single payment market in the EU and improve the current competition and transactional efficiency.
Before the Payment Service Providers Directive (PSD) was introduced in 2007, conducting cross-border transactions within the European Economic Area (EEA) was a complex and costly process.
You had to deal with multiple banks, various currencies, and high transaction fees, making it challenging to expand your business to international customers. The lack of a unified payment system created inefficiencies, making it difficult to compete with larger businesses.
However, with the implementation of the PSD, the process became much simpler. Now, you can use a single payment service provider to manage transactions in multiple EEA countries, reducing transaction costs and currency exchange hassles. This streamlined approach has opened up new opportunities for your small business to expand across borders, compete more effectively, and serve customers across the EEA with ease.
Although the directive was a huge success, the EU felt that there was room for more innovation.The EU amended PSD in 2009 to create the PSD1 framework, which was again amended in 2013 to its current form of PSD2. The current form, PSD2, is widely considered to have ushered in a new era of consumer-centric financial services in the EEA.
You decide to use a budgeting app that provides valuable insights into your spending habits. Using the PSD2 framework, you can now securely link this app to your bank account. This means the app can access your account data with your consent and provide you with more accurate financial advice and budgeting tools.
Consumers now enjoy increased choice, security, transparency, and convenience in their financial transactions.
Yes, PSD2 must sound intriguing to you, but a proper understanding of what PSD2 is is vital in the current scenario when most countries are looking to create a framework similar to PSD2 for international payments.

What is PSD2, and How Does It Work?
The PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2) is a directive released and managed by the European Union to regulate international payment services within the European Economic Area (EEA). The European Union introduced PSD2 to ensure healthy competition, innovation and secure payment process in the European payment industry. PSD2 builds upon the original Payment Services Directive (PSD) and was adopted in 2015, becoming effective on January 13, 2018.
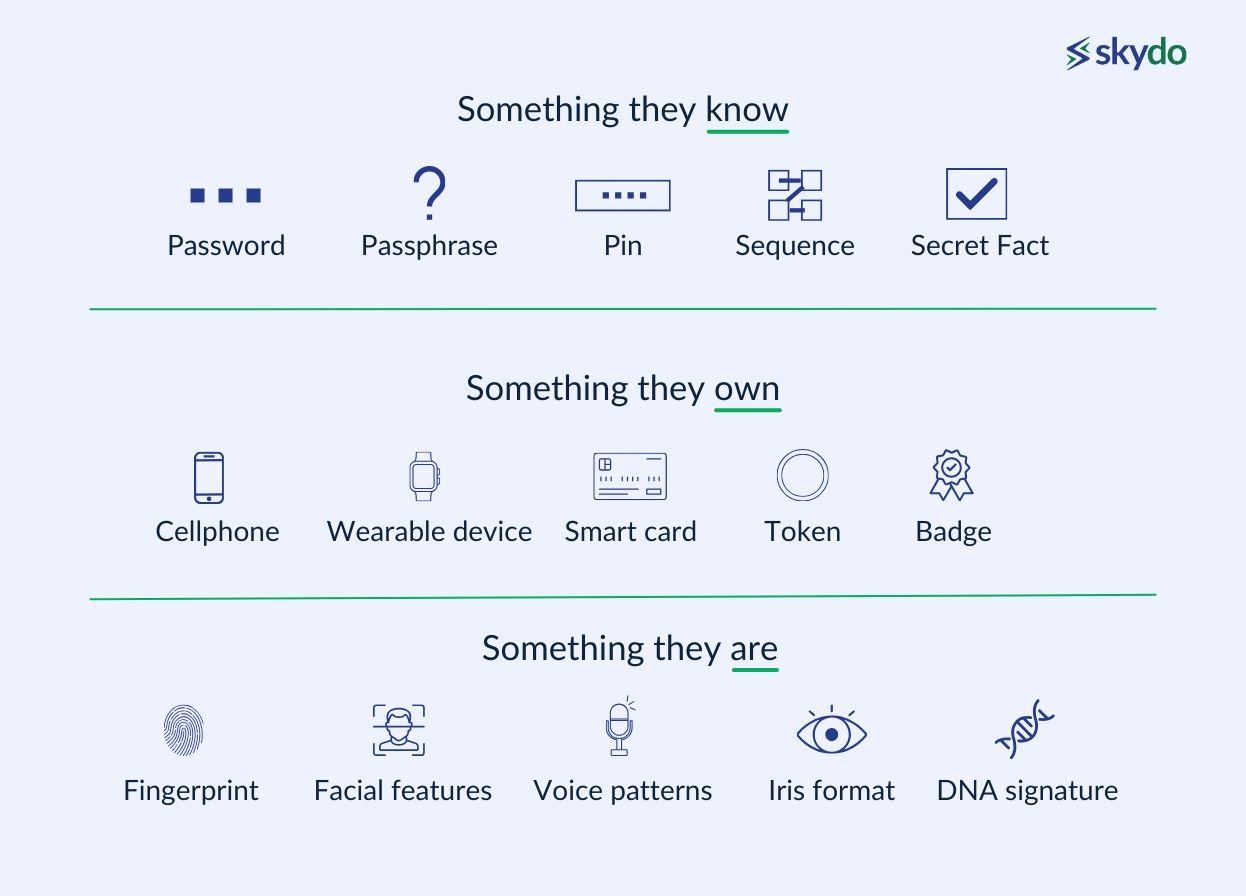
Through the PSD2, the European Union has introduced the Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). SCA completes the transactions by including at least two of the three levels of authorisation: something they know, something they own, and something they are. The transactions require a password or a PIN, a mobile number for OTP and additional security in the form of facial recognition or fingerprint.
PSD2, along with increasing transactional security, has resulted in increased healthy competition by opening up payment services to fintech startups and prompted traditional banks to enhance their offerings. As a result, consumers now enjoy a more user-friendly and cost-effective financial experience.
With a broader range of payment services, consumers can choose a payment service provider with higher customer protection measures and lower transaction fees, further establishing the need for innovation to sustain.
How is PSD2 relevant to Stop Hidden Fees?
PSD2's relevance to stop hidden fees lies in its potential to address opaque pricing practices in international payments. Set to be incorporated into UK law, these regulations prohibit non-transparent pricing methods. Currently, banks and brokers often conceal costs within unfavourable exchange rates, catching customers off guard with undisclosed fees.
PSD2 emphasises the need for consumers to know the 'real costs and charges' associated with cross-border money transfers, echoing the initial Payment Services Directive (PSD). The crucial aspect is whether the government will uphold this commitment, considering past instances of non-compliance. PSD2 presents an opportunity to combat hidden fees and enhance transparency in financial transactions.
Key Provisions of PSD2
- Access to Account (XS2A): Access to accounts through PSD2 provides a direct communication channel between the customer and the merchant’s bank.
Under PSD2, Account Servicing Payment Service Providers (ASPSPs) that maintain customer accounts are compelled to provide Third-party Payment Providers (TPPs) access to customers’ accounts through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Access to accounts allows customers to initiate payments from their bank accounts using third-party services directly.
Imagine you're a regular online shopper, and you're looking to buy a new pair of shoes from an e-commerce website. Before PSD2, you'd typically have to rely on using your credit card, and manually inputting all the details for each transaction, which could sometimes be cumbersome and time-consuming.
With PSD2 in place, things have become more streamlined and secure. As you browse the e-commerce website, you notice a new payment option that says "Pay with Your Bank." You select it.
- Third-Party Providers (TPP) Regulations: PSD2 has also introduced TPP regulations under their PSD2 directive for third-party payment providers within the EEA. It mandates that TPPs obtain proper licensing and meet specific security and transparency requirements.
These include strong customer authentication, secure data communication, data privacy and consent, transparent reporting, and the need to obtain proper licensing. These measures aim to safeguard consumer data, ensure TPP reliability, and maintain the integrity of the payment ecosystem in the EEA.
The Rise of Open Banking
Open banking is a broader concept that refers to the practice of banks and other financial institutions opening up access to their customer’s financial data, with their consent, to third-party providers (TPPs) through secure APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This data sharing allows TPPs to develop new financial products and services.
The concept of open banking started in 2007, with the EU introducing the PSD (Payment Service Providers Directive) to ensure a single payment market in the EU. However, in 2013, the EU proposed an amendment, giving rise to the PSD2. The amended directive introduced the concept of TPPs to give a much-needed push to the opening banking spectrum.
PSD2 serves as the legal framework within the EU that enables open banking practices. It sets the regulatory foundation for secure financial data sharing between banks and third-party providers. Under the PSD2 regulation, the banks are required to provide customers' account information (after their consent) to third-party service providers, allowing customers to:
- Get a consolidated and comprehensive view of their account information using AISPs (Account Information Service Providers).
- Execute online payments through PISPs (Payment Initiation Service Providers).
With PSD2’s push to open banking, the practice allows customers to access a broader spectrum of financial services, including payment initiation, account aggregation and personal financial management. Now, the customer can choose from a host of third-party providers (TPPs) and applications to execute international payments effectively.
Impact on International Payments
Several fintech companies have leveraged the regulatory framework provided by PSD2 to develop efficient and cost-effective international payment services. These companies have utilised access to bank APIs and customer account data to create innovative solutions. Some examples include Wise, PayPal, Skydo, TransferGo etc.
Here is the impact of PSD2 on international payments:
- ‘One Leg Out’ Transactions: ‘One Leg Out’ transactions are where the payer or the payee is outside of the EU and wants to make or receive payments within the EEA. Under PSD and PSD1, such transactions were out of scope. However, with ‘Access to accounts’ and SCA, PSD2 has allowed users to execute ‘One Leg Out’ transactions outside of the EU.
- Mitigate Payment Surcharge: Although PSD and PSD1 revolutionised the payment transactions in EEA, the lack of open banking put the power in the hands of only a few institutions. The resulting transactions were slow and came with high fees, especially surcharges. PSD2 has allowed customers to execute fast international payments with a nominal fee by banning surcharges on card payments made by customers.
Benefits for Consumers
The main motive behind amending PSD and PSD1 to create PSD2 or even introducing such a directive has always been targeted towards the end consumers making international transactions. With PSD2 and open banking, they have experienced several benefits in terms of competition, transparency, cost and security.
Here are the key advantages of PSD2.
- Lower Banking Service Fees Healthy Competition: With the introduction of PSD2 and open banking, the directive has allowed TPPs to be included. Most TPPs are new-age fintech companies and institutions that have created unique and innovative payment solutions.
With numerous innovative payment solutions, customers can now compare and choose the one most suitable for them to streamline cross-border transactions. This healthy competition has also lowered transaction fees and made transactions quicker and more secure.
- Enhanced Security: The impact of PSD2 has been seen majorly in enhancing the transactional and data security for consumers. With the introduction of SCA requirements, which mandate at least a two-factor authentication, PSD2 protects consumers from fraud and unauthorised access.
- Better Transparency for Consumers: PSD2 requires Payment Service Providers (PSPs) to provide clear and transparent information about transaction fees, currency conversion charges, and the terms and conditions of services. The readily available information ensures that consumers better understand the costs associated with their financial transactions.
Global Implications and Future Trends
The introduction of PSD2 by the EU has been a motivating step for global economies as they look to revolutionise their payment industry. Since the EU introduced PSD2, financial experts, policymakers and regulators in other countries are working towards creating a similar framework to promote competition, innovation, and security in financial services. Currently, countries outside the EEA are exploring open banking and how they can leverage it to create a more interconnected global financial ecosystem.
PSD2 has also raised the bar for other countries to ensure better cybersecurity standards and ensure quick processing speed for international payments. Fintech companies that have leveraged PSD2 in EEA are expanding their business to offer other countries better payment solutions with lower transactional fees.
Countries such as Australia, Canada, and Singapore have already introduced or are considering open banking regulations. This chain reaction may continue and expand to countries like India, launching an official directive similar to PSD2.
The increased adaptation of advanced open technologies such as blockchain and digital currencies may play a vital role in the future expansion of PSD2 and open banking. Such technologies, along with international banking partnerships, will play a prominent role in streamlining international payments and cross-border transactions, further transforming the financial landscape.
Conclusion
International payments will only rise in volume as more individuals and businesses establish their global presence. The introduction of PSD2 by the EU and the resulting push to open banking and other customer-protecting measures have positively impacted cross-border transactions and have called for the launching of similar directives in other countries.PSD2’s influence is seen in the proliferation of open banking initiatives, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and improved consumer experiences worldwide. As the financial industry continues to evolve, the principles and trends set in motion by PSD2 will shape the future of banking and payment services on a global scale.
FAQs
Q1. What is a PSD2 directive?
Ans: The PSD2 directive, or Payment Services Directive 2, is a European Union regulation designed to enhance and regulate electronic payment services. It aims to promote innovation, competition, and security in the financial industry by allowing third-party access to banking data through open banking APIs.
Q2. What is PSD2 in open banking?
Ans: PSD2 in open banking refers to integrating Payment Services Directive 2 into the open banking framework. It mandates banks to provide secure access to customer account information to third-party providers, fostering competition and innovation in the financial sector.
Q3. What is PSD2 regulation and what is the impact?
Ans: PSD2 regulation is a set of rules governing payment services within the European Union. Its impact includes increased security measures, open banking initiatives, and enhanced competition as third-party providers gain access to customer data, fostering innovation in the financial sector.
Q4. What is the difference between open banking and PSD2?
Ans: Open banking is a broader concept, while PSD2 is a specific regulation within the European Union. PSD2 mandates open banking practices, requiring banks to share customer data securely with third-party providers. Open banking, in a global context, encompasses various initiatives that promote similar data-sharing practices for innovation and competition.
Q5. According to the PSD2 mandate, what is the maximum number of days to refund the disputed amount?
Ans: The PSD2 mandate stipulates that in case of a disputed transaction, the maximum number of days for a refund is 15 business days from the day the payment service provider receives the complaint.
Q6. How does PSD2 and open banking affect the financial industry?
Ans: PSD2 and open banking positively impact the financial industry by fostering innovation, competition, and improved security. These regulations encourage the development of new financial services and products, driven by collaboration between traditional banks and third-party providers, ultimately benefiting consumers with more choices and enhanced user experiences.
Q7. When does PSD2 come into effect?
Ans: PSD2 came into effect on January 13, 2018, within the European Union. However, individual countries may have slightly different timelines for implementing specific aspects of the directive.
Q8. Is PSD2 only available in Europe?
Ans: Yes, PSD2 is a regulation specific to the European Union. It aims to standardise and enhance payment services within EU member states.
Q9. What does PSD2 mean for banking?
Ans: PSD2 has a transformative impact on banking by promoting competition, innovation, and security. Banks are required to open up their customer data to third-party providers, fostering the development of new services and ensuring enhanced security measures for electronic payments.
Q10. What are PSD2 countries?
Ans: PSD2 applies to all European Union member states. Therefore, the PSD2 countries include those within the EU, as the regulation is designed to create a standardised framework for electronic payment services across the entire union.