The Impact of Open Banking 2024

The traditional banking experience was a revolution upon discovery. However, the integration of technology in banking has resulted in the need to continuously innovate to make the entire transacting experience easier.
Imagine a financial world where you have the power to mix and match services from various providers, creating a truly personalised banking experience. Enter open banking – the current revolution in the financial industry where the talks around the utilities, possibilities, and risks associated with open banking are reaching a fever pitch.
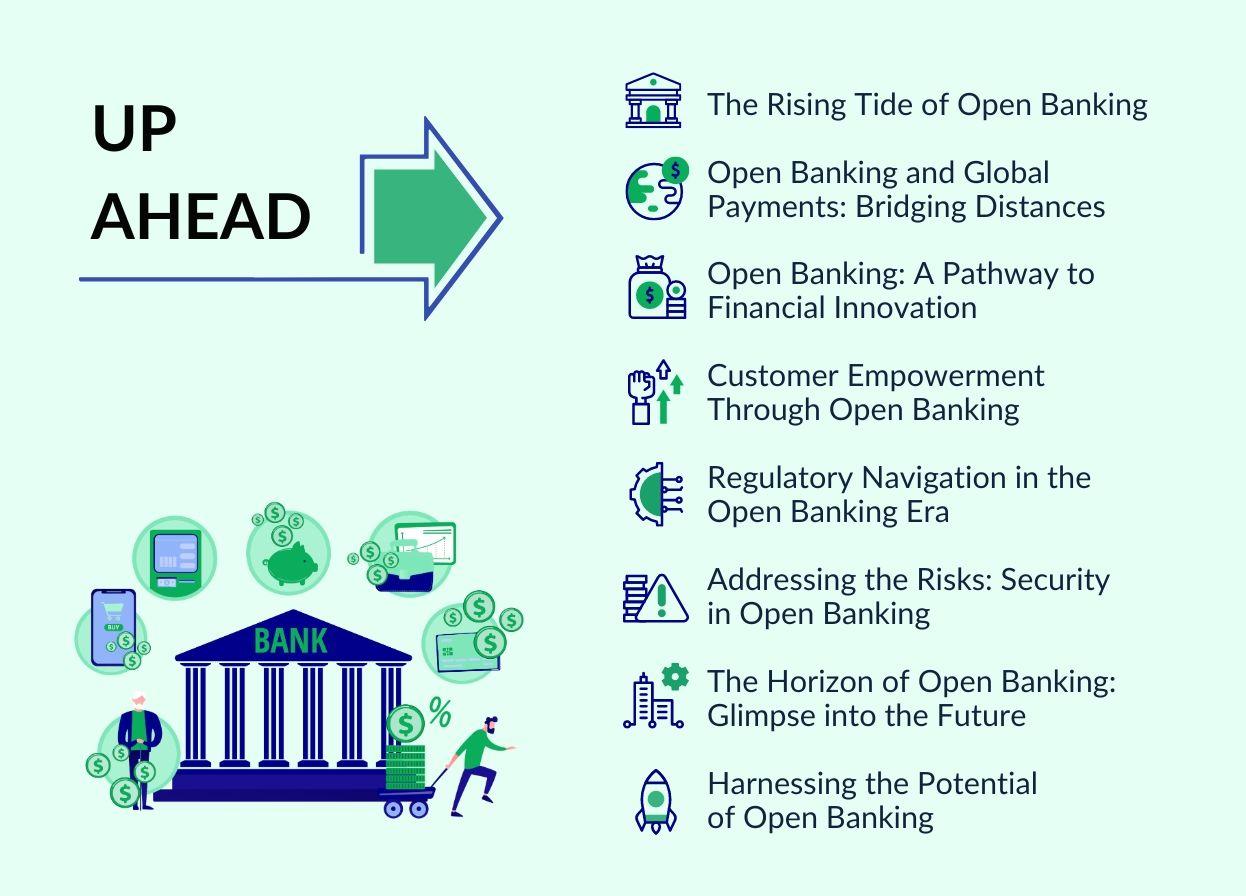
The Rising Tide of Open Banking
Open banking attempts to break the monolithic structures of conventional banks and institutions and bring a ‘mix-and-match’ of services from multiple financial providers catered to the consumers. It is a system where customers can securely share their financial data with authorised third-party service providers through APIs to allow greater collaboration and foster the development of innovative, tailored financial solutions.
Open banking shifts the focus of financial services from a single-bank model to a collaborative approach. It helps securely and effectively leverage consumer data to foster an ecosystem based on data portability and interoperability.
This article aims to address some of these opportunities in the context of cross-border payments and international banking.
Open Banking and Global Payments: Bridging Distances
When expanding globally, businesses face major constraints while navigating payment cultures in different countries. For instance, corporate credit cards are most prevalent in the US, but most of Europe relies on wire transfers.
Payments through ACH (Automatic Clearing Houses) can take days to get authorised. The constant back-and-forth between multiple banks and clearing houses painfully limits and slows the process. There are also specific regulatory abidance for each country that businesses need to adhere to.
Open banking makes it possible for fintech services to serve customers at their homestead. It addresses the fundamental problems in traditional payment mechanisms and eases bank-to-bank payments. It automates manual processes to help customers authorise payments in a few clicks.
Open banking further cuts the fluff involved in international banking transactions to help businesses attain global growth.
For instance, assessment, interchange, and processing fees cost 1.5% to 3.5% of every credit card transaction to merchants in 2020. Open banking cuts out the intermediaries and directly connects customer’s bank accounts. This arrangement saves considerable time and costs for businesses with slimmer margins.
Open Banking: A Pathway to Financial Innovation
Earlier, customers were at the mercy of the banks. Most of the banks provided similar services, often limited in nature. The open banking framework has turned the tide in favour of customers. Fintech service providers compete to build a wide range of products and services that deliver a stupendous experience, ease of use, transparency, and cost efficiency.
Stripe and Braintree have disrupted the payment scenario by granting access to the underserved. In China, WeChat and AliPay are the new digital finance ecosystems serving customers based on their needs.
UPI and mobile wallets are among India's biggest use cases for domestic payment solutions based on open banking. In the US, large banks have struck data-sharing deals with third-party providers. Chase partnering with Intuit and Wells Fargo with Xero and Finicity are a few examples.
Customer Empowerment Through Open Banking

Open banking further empowers customers through data ownership and control. Fintech startups, technology companies, and financial institutions are synergising their efforts to enhance the overall customer experience by leveraging banking data.
Customers can enjoy seamless transactions, personalised financial insights, and transparent pricing frameworks while fully controlling with whom they share their financial data and to what extent.
APIs allow seamless integration of financial services such that businesses get a personalised suite of services for international dealings and cross-border payments. Many fintech service providers provide the dual benefit of the ease and simplicity of bank transactions and cutting-edge services like e-wallets, easy remittances, and currency exchanges.
In fact, the focus of such services and platforms is to provide their customers with the best user experience and innovative financial solutions. Yet, the pressing question remains about the regulatory and security aspects of this revolutionary banking avenue.
Regulatory Navigation in the Open Banking Era
Most apps and platforms based on open banking are built on robust security protocols and comply with their country's stringent data protection regulations. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an important EU law that governs data sharing.
PSD2, another set of data protection rules in Europe, explicitly grants the authority to share data to account holders instead of banks. India also passed its new data protection bill in the recently concluded monsoon session. Many regional regulatory frameworks mandate consumer protection and privacy to the highest degree.
Third-party service providers need to ensure compliance at multiple levels as different data requires different levels of security. Data sharing is mostly risk- and permission-based in financial services. It must have proper audit trails per the regulations and risk management guidelines.
Fintech services can follow enhanced KYC procedures, identity validation, and fraud detection for compliance and regulatory adherence.
Addressing the Risks: Security in Open Banking

Open banking is based on data sharing of personal and sensitive information. Securing such information is the elephant in the room, which needs addressing. It poses risks in the form of increased exposure and vulnerability of data toward potential breaches, frauds, misuse, and hacks.
Fintech services and platforms must implement robust security measures and data protection guardrails such as encryption, monitoring, authorisation, and authentication. Measures such as two-factor authentication, KYC norms, dedicated age verification tools, AML solutions, and in-built security walls enhance data protection and eliminate manipulation or tampering.
The Horizon of Open Banking: Glimpse into the Future
A KPMG report states the banking industry will see more changes in the next decade than it has in the past 100 years.
The Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) with open banking, powered by custom AI solutions, will help customers embark on a journey of autonomous financial experiences. Fintech services and banks will have a greater insight into their customers’ lives, which calls for greater trust and robust security mechanisms. New business models and use cases for financial services will emerge to redefine the service provider-customer relationship.
Consolidation of services into a ‘super app’ will occur as AI and other emerging technologies interface with open banking solutions. AI will play a critical role in helping customers overcome their low levels of financial literacy. Technologies such as IoT and Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) will create trustless models of customer engagement and automation in financial services.
Businesses need to accept the change if they seek growth and relevance readily. Along with this technology adoption, IT exporters and international businesses need to be at the forefront of compliance and security to provide their customers with the best experience and smoothly functioning business processes.
Harnessing the Potential of Open Banking

Currently, the world relies on heterogeneous modes of payments, and abiding by all can get time-consuming and expensive for small-scale IT exporters and businesses. Open banking is revolutionising the banking sector and creating opportunities for businesses to grow globally.
Furthermore, cross-border payments are expected to reach $250 billion by 2027. Consequently, the need to smoothen the creases and bumps in the international payments process is more pertinent than ever.
Fintech solutions like Skydo, driven by open banking, will be crucial in building and streamlining collaborative international payments infrastructure from scratch.