What Is Purpose Code and Why Is It Required?

As an exporter or freelancer dealing with global clients, using the wrong purpose code can cause major problems—like transaction cancellations or even RBI investigations.
But before we dive into the consequences, let’s first break down what is a purpose code and why it’s so important.
What Is Purpose Code?
A purpose code is a specific alphanumeric code assigned to transactions, indicating the nature and purpose of the fund transfer.
There are two types of purpose codes, purpose code for inward remittance and purpose code for outward remittance. By assigning a purpose code to a transaction, exporters clarify the intended use of the funds, aiding regulatory authorities in monitoring and regulating cross-border financial flows and ensuring regulatory compliance
When Do You Need to Use the Purpose Code?
Purpose codes are mandatory for Indian exporters engaging in international transactions. These codes are required when receiving or making payments for goods and services across borders.
Types of Purpose Codes
Purpose codes differ based on whether you are receiving or making an international transfer.
1. Purpose Code for Inward Remittance
These purpose codes are used when you are receiving an international transfer. These purpose codes signify the purpose for which you are receiving the transfer. Purpose codes for inward remittance start with P followed by the respective numericals.
For example, P0802 is a purpose code for inward remittance that is used when an exporter receives a foreign payment in exchange for software consultancy or implementation service, provided to a foreign client.
You can find some of the popular purpose codes for inward remittance right here.
2. Purpose Code for Outward remittance
As the name suggests, these purpose codes are used while making an international transfer. These purpose codes signify the purpose for which you are making the transfer. Purpose codes for outward remittance start with S followed by the respective numericals.
For example, S0301 is a purpose code for outward remittance that is used when sending money abroad for business travel.
Role of the Reserve Bank of India
The RBI assumes a key role in overviewing and regulating international transactions. The key aspects of the RBI's role include:
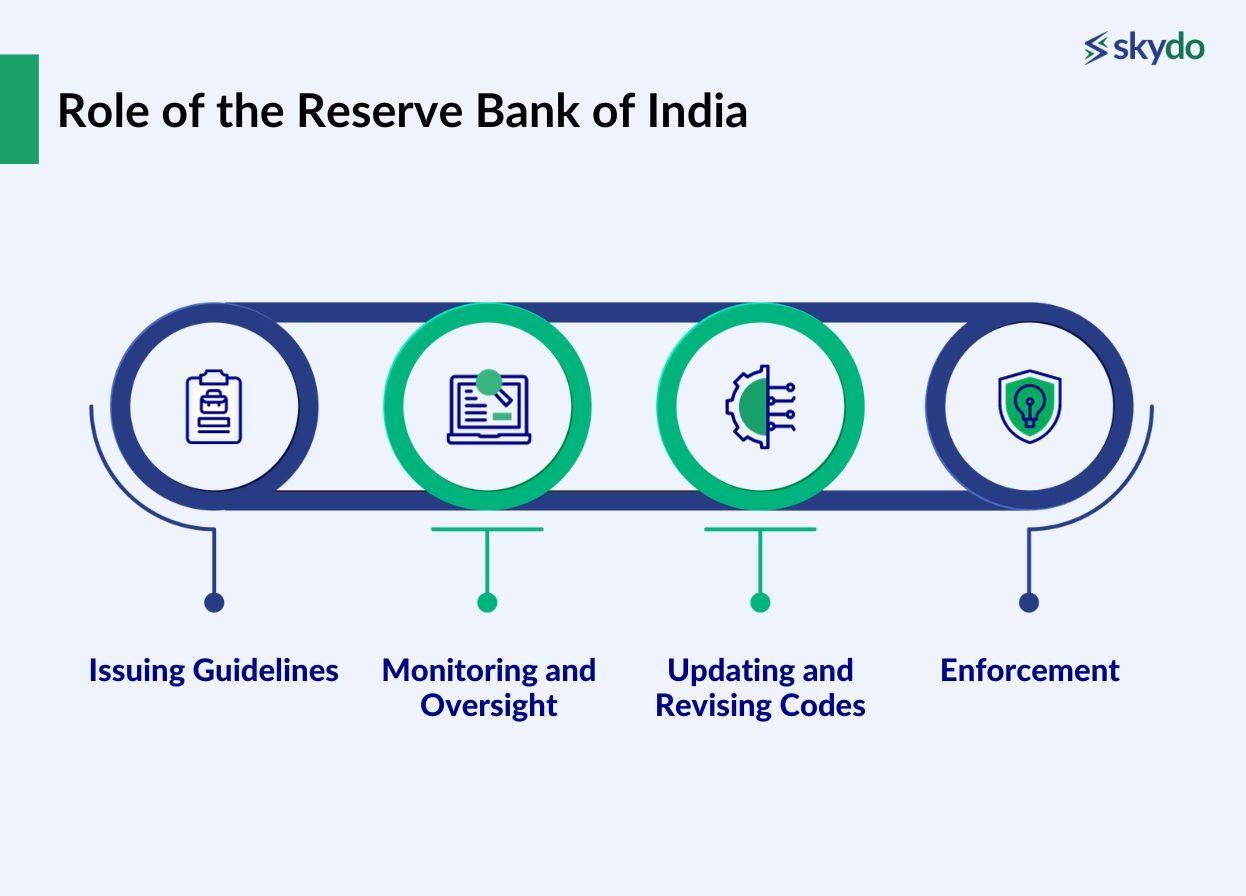
- Issuing Guidelines: The RBI has issued comprehensive guidelines and circulars that define the purpose codes, their usage, and the regulatory requirements surrounding international transactions.
- Monitoring and Oversight: The RBI employs a sophisticated real-time monitoring system overseeing transactions conducted by Indian exporters and institutions.
- Updating and Revising Codes: The RBI periodically updates and revises purpose codes to align with evolving global financial standards.
- Enforcement: The RBI enforces compliance with purpose codes through audits, inspections, and penalties for non-compliance.
Compliance Requirements for Indian Exporters
Indian exporters engaging in international transactions must adhere to specific compliance requirements related to purpose codes. Key considerations include:
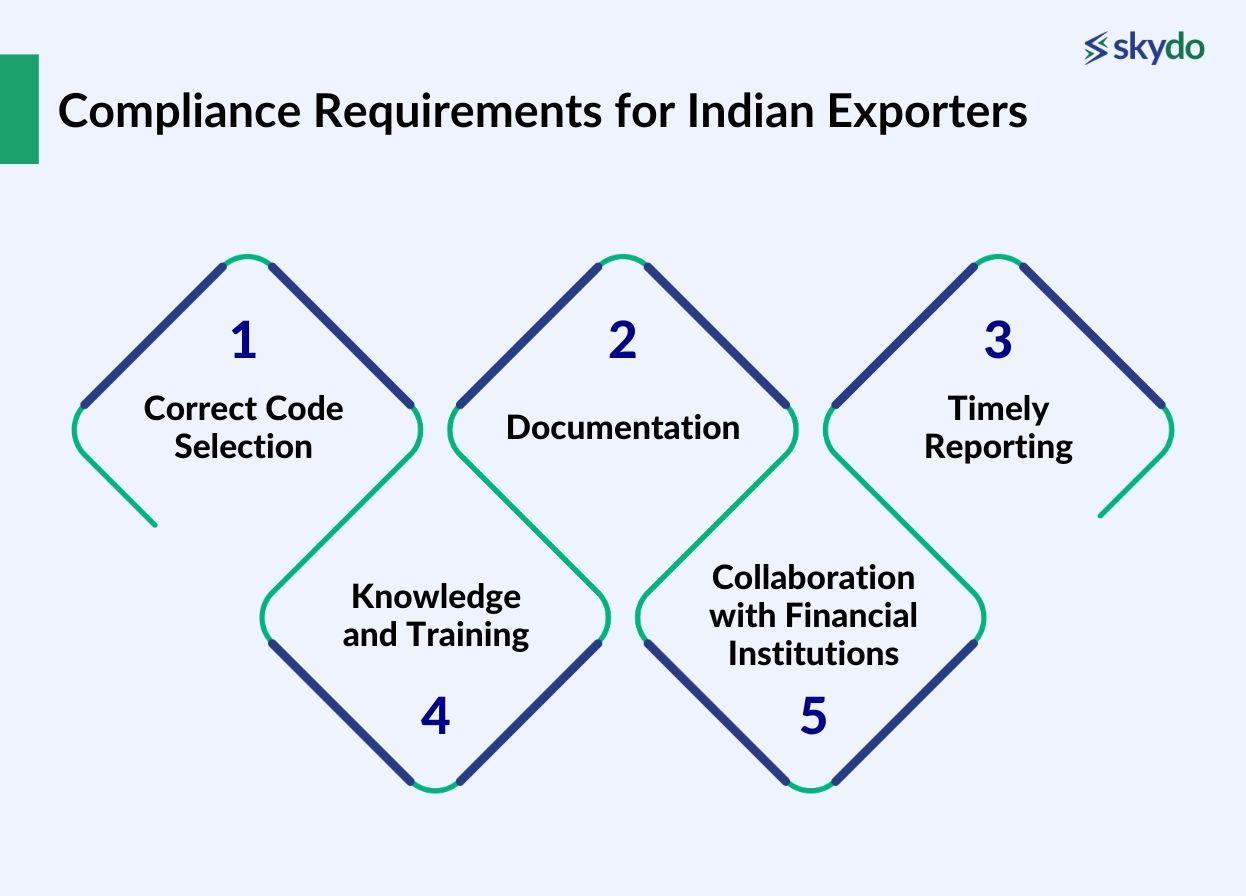
- Correct Code Selection: Exporters must select the appropriate purpose code for inward remittance for each transaction, ensuring that it aligns with the nature of the financial activity.
- Documentation: Exporters should keep records of purpose codes associated with each transaction, supporting documents, and relevant communication.
- Timely Reporting: As an exporter, ensure you report your international transactions to regulatory authorities on time to avoid future legal complexities.
- Knowledge and Training: Exporters should invest in training and awareness programs for their staff to ensure they fully understand compliance obligations.
- Collaboration with Financial Institutions: Always consult your bank or relevant financial institution to clear any doubts regarding purpose codes.
Significance of Purpose Code for Inward Remittance
For exporters, sharing the correct purpose code with their banks is crucial for receiving international payments especially concerning countries like China. . An incorrect purpose code can result in delays or even cancellation of the transaction. And, while it is not very common, in some instances, sharing the incorrect purpose code can also lead to compliance issues later on for exporters, highlighting the importance of adherence to regulations.
Beyond these practical reasons, purpose codes are instrumental in monitoring global payments and preventing suspicious activities. Here’s how:
Facilitating Accurate Tracking of Foreign Exchange Transactions
The purpose codes provide a standardized framework for financial institutions and regulatory bodies to track the flow of funds precisely.
Role in Preventing Financial Fraud and Ensuring Transparency
Purpose codes ensure that financial transactions align with the intended purposes declared by Indian exporters. It also helps detect and prevent illicit activities such as money laundering and fraudulent financial practices.
How do I know my purpose code?
Finding the right purpose code for inward remittance can be confusing due to technical jargon and overlapping descriptions. Having assisted over 3,000 customers, we understand this challenge well.
Consider the following factors when selecting the appropriate purpose code
Factors influencing the choice of Purpose Code
- Nature of Transaction: It involves goods and services, advance payments, non-resident deposits, or other specific financial activities.
- Industry Specifics: These codes could be for IT, pharmaceuticals, or manufacturing sectors.
- Regulatory Guidelines: Ensure their alignment with the RBI guidelines and international regulations.
Steps Involved in Determining the Appropriate Purpose Code
- Classify transaction as payment or receipt: The RBI has two separate lists for payment and receipts. Pick the list based on the nature of your transaction.
- Look under the appropriate section: Based on the nature of your business services, choose the right section and code from the list. It can be accessed here.
- Consult your bank/ advisor: Finally, seek guidance from your banking partner or financial advisor to reconfirm your selected code.
It’s important to choose the right code to avoid legal complications, delays or freezing of payments, and penalties from the regulator.
You can check out the purpose code finder tool to know the correct purpose code for inward remittance.
Common Challenges Faced by Indian Exporters Regarding Purpose Code
- Lack of Awareness: Many exporters don’t understand the implications and requirements associated with Purpose Codes, leading to unintended violations and bumps in international transactions.
- Complexity in Classification: Diverse trade activities make it challenging for exporters to categorize their transactions precisely. Misclassification can lead to regulatory scrutiny, delays, and financial repercussions.
- Technological Hurdles: Submitting Purpose Codes efficiently often requires advanced technological infrastructure, which may not be universally accessible.
- Changing Regulatory Landscape: Exporters must proactively stay informed about regulatory updates and adapt their processes.
How to Ensure Compliance With Purpose Codes
- Education and Training: Train your accounts and finance team. They must know how each of your goods/services must be classified.
- Streamlining Processes: Create checklists and documents to build foolproof processes and avoid unnecessary delays due to human errors.
- Investing in Technology: Automation and digital tools can significantly simplify and automate the classification of transactions, reducing the likelihood of errors. Invest in modern systems facilitating seamless Purpose Code submission can improve efficiency and compliance.
Tips for Avoiding Errors and Ensuring Compliance
- Double-Check Information: Exporters should implement a maker-checker mechanism on all information related to Purpose Codes.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Establishing a practice of weekly/ monthly audits and reviews is essential to identify and correct errors.
- Stay Informed about Regulatory Changes: Keep track of RBI notifications to stay posted on the latest changes and updates.
- Seek Professional Assistance: For complex transactions, professional advice can be invaluable. Exporters can engage with consultants or experts well-versed in international trade regulations.
Conclusion
For Indian exporters, RBI Purpose Codes are key to transparent and compliant cross-border transactions. They ensure that funds are used correctly and regulatory requirements are met, while incorrect usage can lead to transaction rejections.
To navigate these complexities, follow best practices: train your team, use the best digital tools, and stay updated on regulatory changes.
How do I know my purpose code?
You can refer to RBI's list of purpose codes to know the right purpose code for your transaction. You can also use our purpose code finder tool right here to find the correct purpose code for your inward remittance.
What is the inward remittance purpose code?
What is the purpose code for foreign outward remittance?