Exploring Sole Proprietorship: Is It the Right Business Structure for You?

You're sitting at your favourite coffee shop, doodling your latest business idea on a napkin. You envision turning your passion into a full-fledged venture. Whether it is crafting artisanal jewellery, offering consulting services, or selling your signature baked goods, the appeal of starting a sole proprietorship is absolute.
The world of entrepreneurship beckons, and the journey begins with a single step – understanding the legal and regulatory landscape that comes with it.
Hold on to your napkin and read on!
What is a Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a business structure in which a single individual owns and operates without the involvement of other individuals or partners. A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of business and is quite common among solo entrepreneurs and small businesses.
The owner has complete control and decision-making authority over the business. A sole proprietorship has no legal distinction between the owner and the business entity.
Some features that make sole proprietorship an attractive business structure include the following.
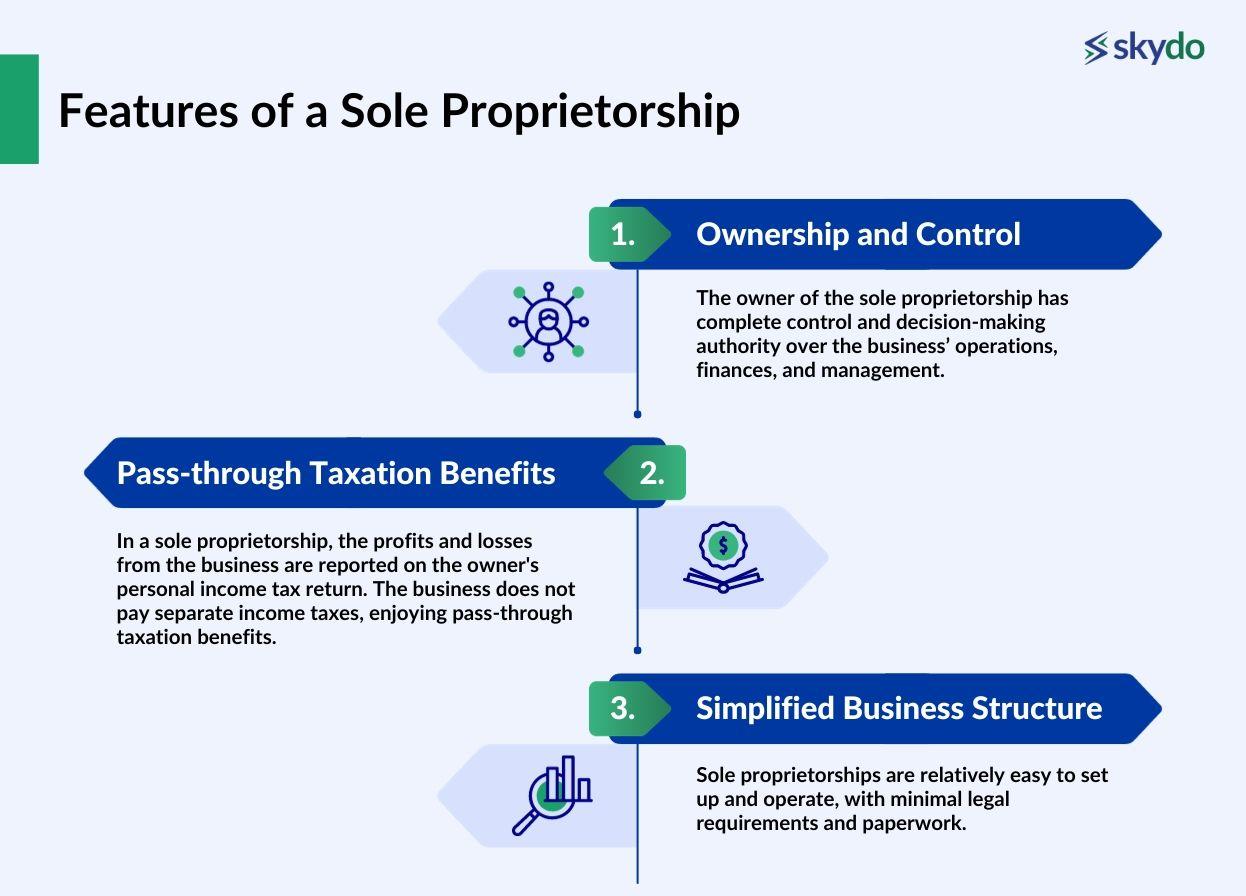
- Ownership and Control: The owner of the sole proprietorship has complete control and decision-making authority over the business’ operations, finances, and management.
- Pass-through Taxation Benefits: In a sole proprietorship, the profits and losses from the business are reported on the owner's personal income tax return. The business does not pay separate income taxes, enjoying pass-through taxation benefits.
- Simplified Business Structure: Sole proprietorships are relatively easy to set up and operate, with minimal legal requirements and paperwork.
How Do You Start a Sole Proprietorship In India?
Sole proprietorships suit individuals and small businesses with limited risk exposure and relatively simple operations. However, the business has to adhere to the legal and regulatory framework set by the Indian government to ensure legal operations. The process starts with the regulatory and legal steps to start a business with you as its sole owner.
Let’s start with the personal front for starting a sole proprietorship.
1. Developing Your Business Concept
Developing your business concept involves refining your idea and creating a clear plan for operating your business. The business idea should emerge after you identify your interests, skills and passion. Find answers to questions like–
- What are you passionate about?
- What are you good at?
- What problems or challenges in the market do you see an opportunity to address?
- What unique skills or expertise can you bring to your business?
- Are there any industry trends or market gaps that align with your interests and skills?
Choose the business concept that aligns the most with your interest and expertise.
2. Market Research and Analysis
You may create a business idea based on your passion, expertise and interest. However, backing it through extensive market research and analysis is equally important.
The step involves researching and analysing the target market, the current competition, the demand and supply factors, investment requirements and growth potential. One of the best ways is to execute a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to assess your business's internal strengths and weaknesses.
Naming Your Business
Naming your business is critical in establishing your brand identity and creating a memorable impression on your target audience. The name you choose must be unique and must relate to the business idea and the target customers.
Take the example of Zomato, Ola, Oyo, etc. Although the brand names have a certain meaning, they are unique in the sense that the customers have made them synonyms for their respective industries. However, you must check the legal requirements and restrictions for business names in your jurisdiction before naming your business.
The following steps define the legal and regulatory actions to register your sole proprietorship. These steps contribute highly to giving a legal identity to your business.
Legal and Regulatory Steps
1. Business Registration
You must register your business based on the company name and registration process defined by the Indian government and other regulatory bodies. The steps involved in business registration are:
- Obtain a PAN (personal PAN Card of the sole proprietor)
- Udhyog Aadhaar (if applicable)
- IEC Code
- MSME Certificate (if applicable)
- Obtain the Registration Certificate under the state’s Shops and Establishment Act where you plan to start the business.
- Register for GST if the business turnover exceeds 20 lakhs. You can do this in the year your business turnover exceeds the threshold.
The 20 lakh limit is set for intra-state supply of goods and services. However, if you execute a trade outside the state, you must register for GST. Furthermore, you should open a bank account for your business once registered.
2. Taxation Compliance/Consideration
Once the business is registered, you must take further steps to complete the business’s taxation compliances. Obtain a TIN (Taxpayer Identification Number) for your business’ easy identification by the revenue department.
You can manually fill out Form SS-4 and mail it to the Indian Revenue Service or log in to the respective VAT portal of the state government to submit the application form online. It is mandatory to mention the TIN while making state-level or interstate sales.
3. Business Insurance
Business insurance is a type of coverage designed to protect businesses from financial losses and liabilities that may arise during their operations. Business insurance is vital for a sole proprietorship as the owner has unlimited personal liability for the business's debts and legal obligations.
This means that if the business incurs debts or faces legal issues, the owner's assets are at risk to satisfy those obligations.
There are numerous business insurance policies, such as property insurance, fidelity guarantee insurance, commercial vehicle insurance, etc. However, you must consider liability cover insurance to protect your assets in case of business financial obligations.
This wraps up the legal and regulatory steps involved in the legal steps to starting a business (sole proprietorship) in India. But what about protecting your goods and services and managing the operations and resulting transactions?
Intellectual Property Protection
Once you have registered your business and have developed your goods or services, you must protect them under intellectual property rights. In India, numerous acts govern intellectual property, such as the Trade Marks Act of 1999, the Patents Act of 1970, The Copyright Act of 1957, etc.
Before selling your goods or rendering services, you should obtain relevant copyrights, trademarks, and patents from the respective authorities to protect your business’ various intellectual properties.
Contracts and Agreements
Written agreements are essential in sole proprietorships, just as in any other business structure. Written agreements clearly outline a business’ terms, conditions, and expectations and can serve as legally binding contracts. Furthermore, when you operate a business, you create or sign numerous contracts related to services, clients, vendors or suppliers.
You should create and keep written agreements and contracts to enforce the terms and protect the rights and interests in case of any legal dispute.
Record Keeping and Compliance
Maintaining business operations calls for booking and accounting, as they are an essential part of compliance for a registered sole proprietorship. Systematically record and organise all the financial transactions, such as business income, assets, and expenses.
Then, you must interpret and analyse the recorded financial data and prepare relevant financial statements such as balance sheets, cash flow statements and profit and loss accounts. Such record-keeping helps determine the tax liability and ensure you file your taxes within the mentioned deadlines.
Pros and cons of sole proprietorship
Advantages of a Sole Proprietorship Business
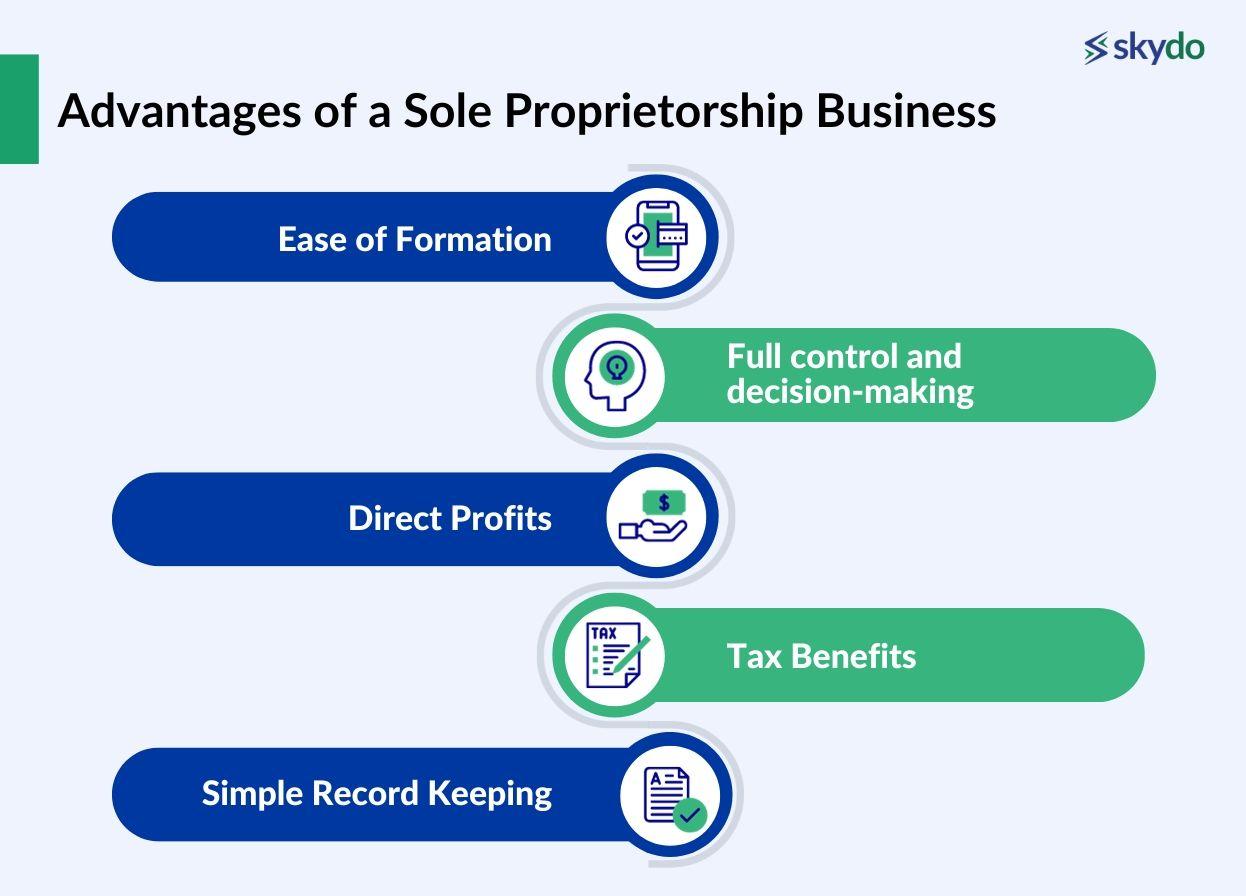
A sole proprietorship is the simplest business structure that allows a person to manage and operate the company as they like. Below are some of the fundamental advantages of a sole proprietorship business.
1. Ease of Formation
Sole proprietorships do not require an extensive registration process, including complex paperwork and a long waiting period. Furthermore, in many cases, it is optional to register a sole proprietorship, making it an attractive option for individuals looking to start a small business without a significant upfront investment.
2. Full control and decision-making
One of the best pros of sole proprietorships is that the business owner has complete control, ensuring quick decision-making and better adaptation to market change.
3. Direct Profits
In other business structures, such as partnerships, the partners must share the realised profits in a specific ratio, significantly lowering the individual profit margin. However, in sole proprietorships, a single individual owns the business and is the sole receiver of all the profits.
4. Tax Benefits
Sole proprietorships can reap the benefits of pass-through taxation, allowing owners to record business income and expenses on their tax returns.
Unlike corporations, pass-through taxation also ensures that the income is not taxed twice. Additionally, they may be eligible for deductions and credits that can reduce the overall tax liability.
5. Simple Record Keeping
Unlike corporations or limited liability companies, sole proprietorships are small-scale, resulting in less complex resource management and financial data.
Record keeping and accounting for sole proprietorships are less complex than larger businesses, saving valuable resources such as time and money on administrative tasks.
Disadvantages of a Sole Proprietorship Business
An entrepreneur must consider the disadvantages of a sole proprietorship business before choosing it as a business structure.
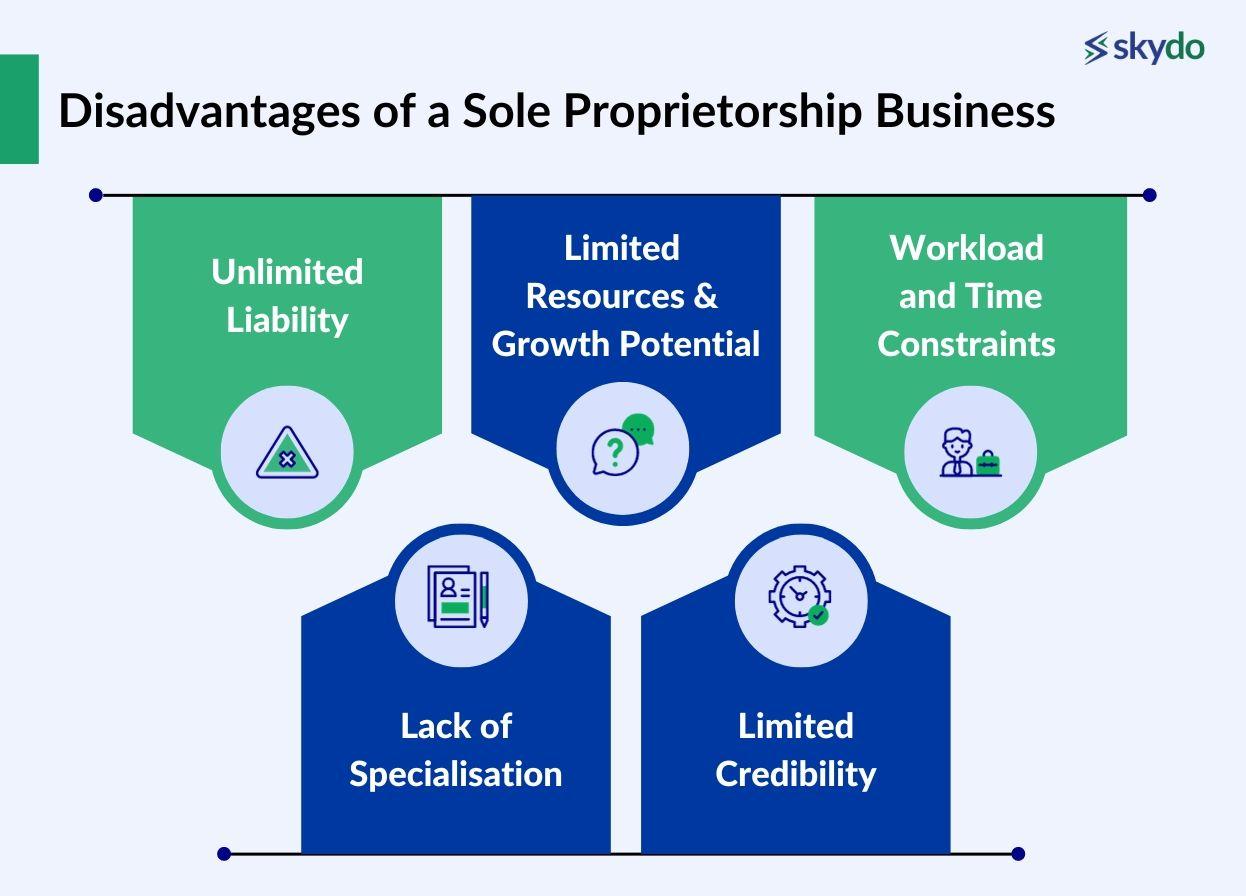
1. Unlimited Liability
Unlimited liability means that if the business incurs debts it cannot repay, creditors can seize the owner's assets, including their home, savings, and other personal property.
Furthermore, creditors can file a criminal case under unlimited liability if the owner fails to repay the debt or fulfil other financial obligations.
2. Limited Resources and Growth Potential
Sole proprietors face numerous difficulties in raising external capital through investors or by availing loans. Investors or financial institutions hesitate to offer credit owing to the limited repayment capacity and the complex procedure of seeking repayment under unlimited liability.
3. Workload and Time Constraints
Since the sole proprietor is solely responsible for managing and operating the business, it may become difficult to manage every aspect, such as accounting, marketing, or legal compliance. The added workload over time and time constraints due to a single owner may force the business to lose out on growth and struggle to support and scale.
4. Lack of Specialisation
Running a business, irrespective of its nature and size, requires skills and expertise in planning, organising, controlling, sustaining, regulatory compliance, filing taxes, etc. A sole proprietor may be an expert on a specific business aspect but struggle to manage other aspects due to a lack of proper knowledge.
5. Limited Credibility
The creditworthiness of sole proprietors is directly related to their capital because of unlimited liability. However, some suppliers and partners may perceive sole proprietorships as less stable or credible than larger, incorporated businesses. This perception can affect attracting clients and establishing strong business relationships.
Sole Proprietorship vs. PLC vs. Partnership
Sole Proprietorship, PLC (Private Limited Company), and Partnership are different business structures. A sole Proprietorship is a one-person business without legal separation from the owner, making them personally liable for debts and obligations.
PLC is where two or more stakeholders are the business owners. They have limited liability, which protects the owners' assets from business debts while maintaining a flexible management structure.
Partnerships involve two or more individuals sharing ownership and responsibilities, but they share personal liability for business debts. Choosing between these structures depends on factors like liability protection, management style, and tax implications, each offering advantages and disadvantages for entrepreneurs and businesses.
Planning for Growth
Your business must earn profits and tackle the dynamic market for sustainability, right? While sole proprietorships are typically smaller in scale, they can still experience significant expansion and success with proper planning and execution.
Regularly access your business’s financial health and capital requirements. If you fall short, explore external funding options such as business loans. Furthermore, an in-demand business may require further expertise on various other company aspects, requiring you to hire experts with relevant skills.
Marketing is vital to business growth, which you can attain by leveraging social media channels to create brand awareness and goodwill.
Managing the Challenges
Similar to every other business structure, a sole proprietorship always has its set of pros and cons. Since the pros of sole proprietorships are value addition factors to the simplest form of business structure, it is essential to manage the cons to ensure a healthy balance.
Managing the challenges of a sole proprietorship requires careful planning, proactive strategies, and a willingness to adapt to changing circumstances. Here are some ways to address the challenges associated with sole proprietorships.
- Minimising Liability Risk: The owner of a sole proprietorship has to accept the unlimited liability associated with the business structure. However, owners can purchase liability or business insurance to protect their assets in case of financial obligations and ensure business continuity.
- Strategies for Growth and Resource Management: Managing resources is pivotal for creating a blueprint for future sustainability and growth. It details the effective management of all the business resources and how the owner can use them to tackle limited funding availability.
- Time management and delegation: Managing a sole proprietorship is considered an individual business. However, handling every aspect of the business alone may become overwhelming, resulting in mismanagement and a high workload.
One of the best ways to ensure effective time management is to list all the tasks based on their priority and delegate the less important tasks by hiring other helpers.
Conclusion
Sole proprietorships offer entrepreneurs a unique path to business ownership, characterised by autonomy and simplicity. However, they come with their own set of challenges that require careful management and consideration. Before starting a sole proprietorship, it is always beneficial to understand the pros and cons of a sole proprietorship, as these factors are crucial to adopting or passing on this business structure.
Ultimately, the path of a sole proprietor is rewarding for those willing to embrace its responsibilities and challenges. With dedication, perseverance, and a well-thought-out strategy, individuals can turn their sole proprietorships into thriving enterprises fulfilling their entrepreneurial dreams.
FAQs
Q1. How Do You File Taxes As a Sole Proprietor?
Ans: A sole proprietor files taxes by reporting business profits and losses on their personal income tax return. This process is known as pass-through taxation, where the business doesn't pay separate income taxes. It allows for simplified tax reporting and can result in tax benefits for the owner.
Q2. Why is sole proprietorship the best form of business?
Ans: Sole proprietorship is often considered the best form of business for its simplicity and complete control it offers to the owner. Its advantages include ease of formation, direct profits, and simplified record-keeping. However, its drawbacks include unlimited liability and limited growth potential.
Q3. How to name a sole proprietorship business in India?
Ans: To name a sole proprietorship business in India, choose a unique and meaningful name that aligns with your business idea and target customers. Check for legal requirements and restrictions on business names in your jurisdiction before finalising it.
Q4. How to register a business name for a sole proprietorship?
Ans: Registering a business name for a sole proprietorship involves complying with government regulations and obtaining necessary permits and licenses. The precise steps may include obtaining a PAN card, Udhyog Aadhaar, IEC code, MSME certificate, and registering for GST, depending on your business's nature and turnover.
Q5. What are the different options for expanding sole proprietorship business?
Ans: To expand a sole proprietorship business, you can explore options like obtaining external funding through loans or investors, hiring experts in areas where you lack expertise, and utilising social media marketing to increase brand awareness and customer reach.
Q6. When the owner of a sole proprietorship dies, what becomes of the business?
Ans: When a sole proprietor dies, the fate of the business depends on the owner's will or estate planning. If the business is specified in legal documents, it can be passed on to heirs or beneficiaries. Otherwise, it may need to be sold or closed.
Q7. What is one of the biggest drawbacks to starting a sole proprietorship?
Ans: Unlimited liability is the biggest drawback of starting a sole proprietorship. It means the owner's assets are at risk to satisfy business debts and obligations. Creditors can seize the owner's personal property, including their home and savings, in case of financial difficulties or legal issues.